Machine Learning By Andew Ng - Week 7
Large Margin Classification
Optimisation Objective
-
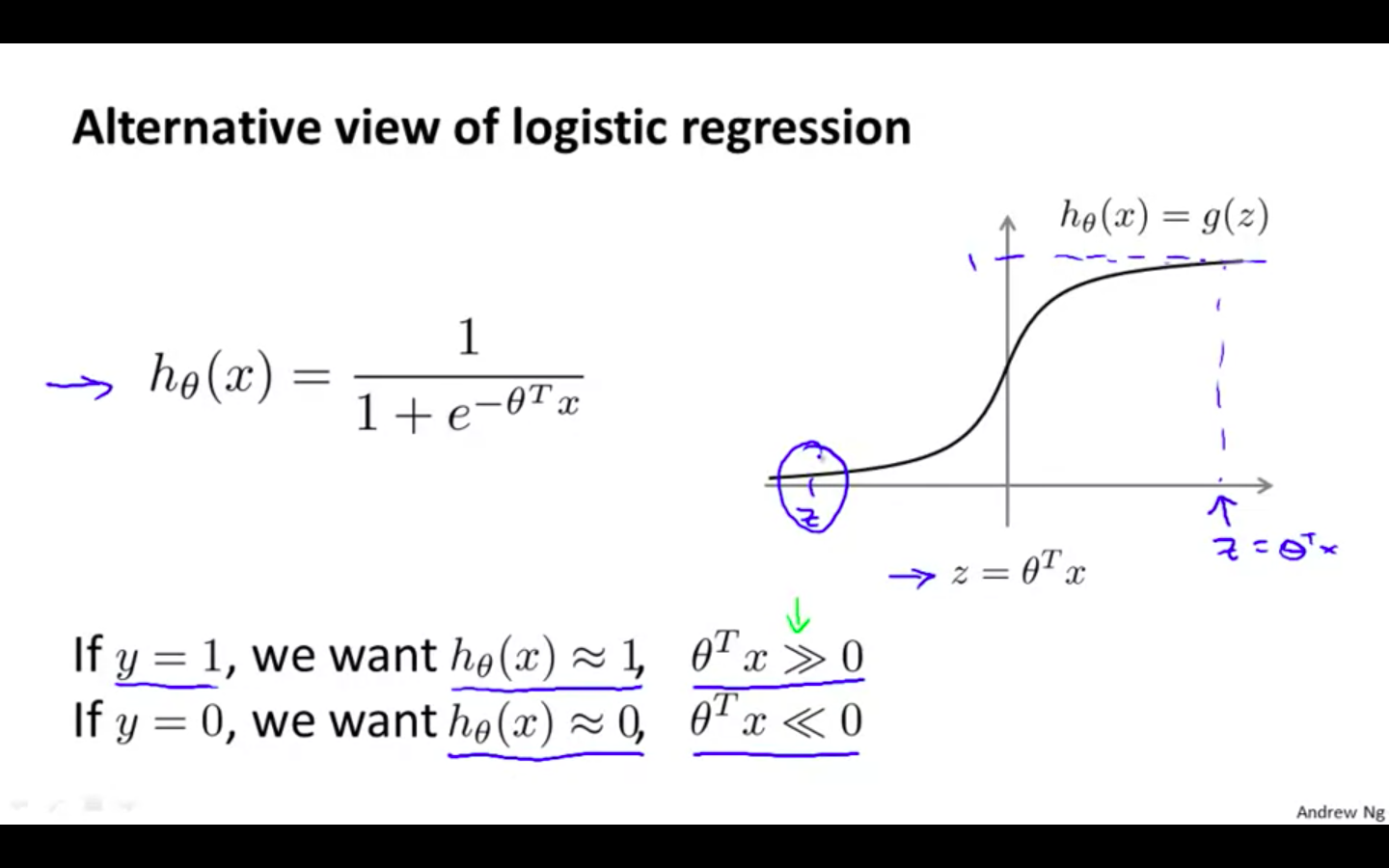
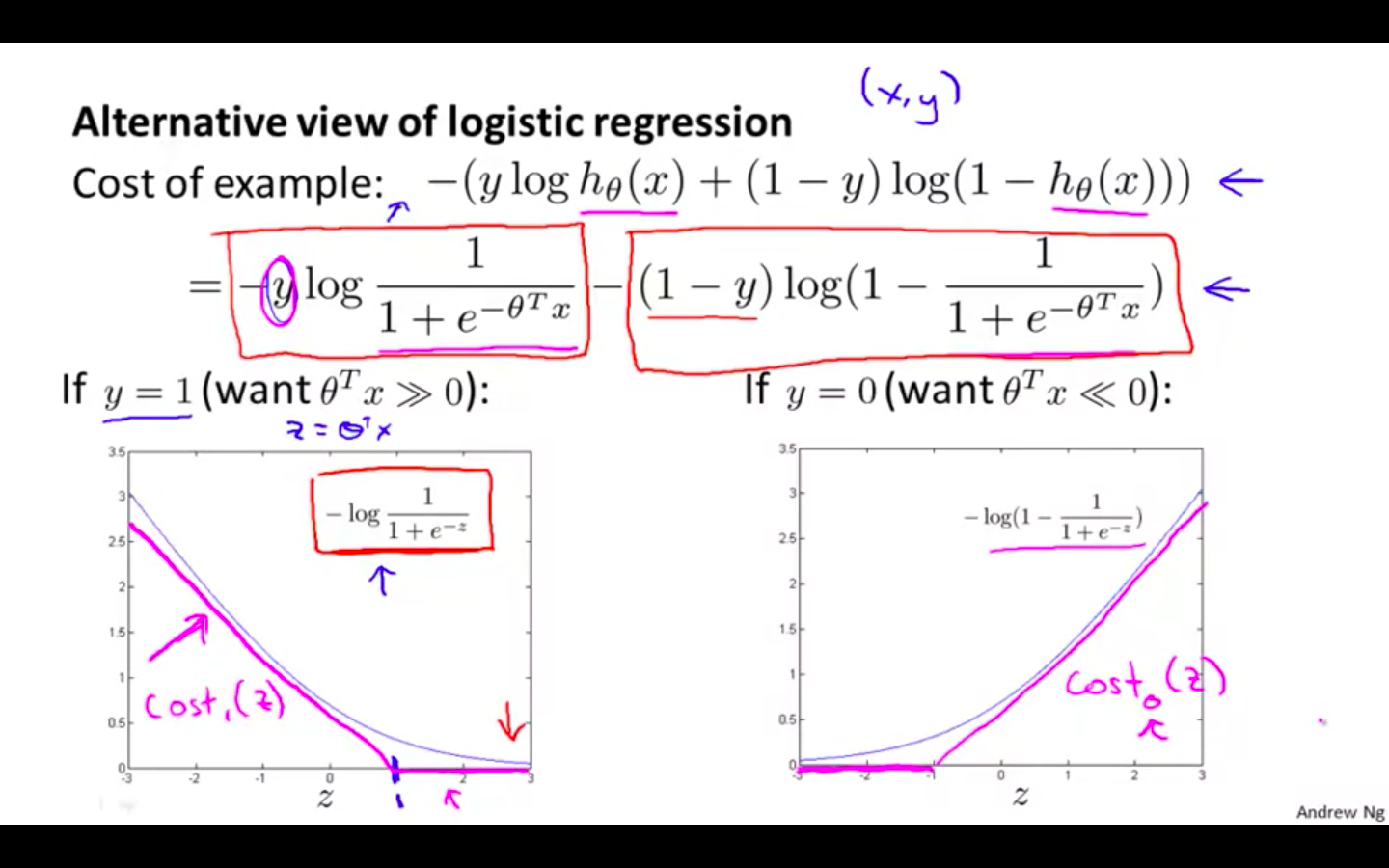
Alternative View Of Logistic Regression
-
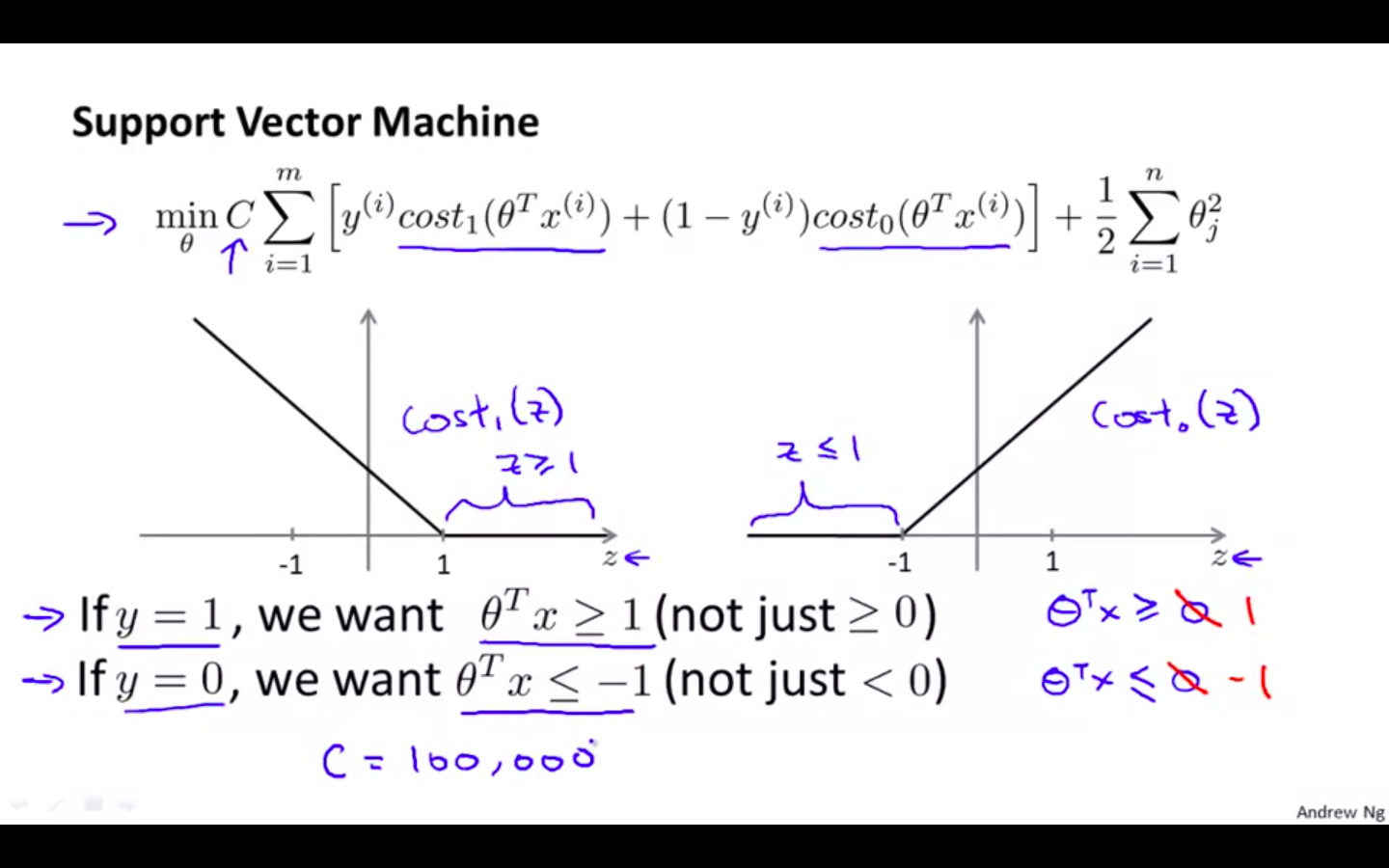
If y = 1, h(x) should be similar to 1, theta^T x » 0
-
If y = 0, h(x) should be similar to 0, theta^T x » 1
- Graph plotting of function z
-
-
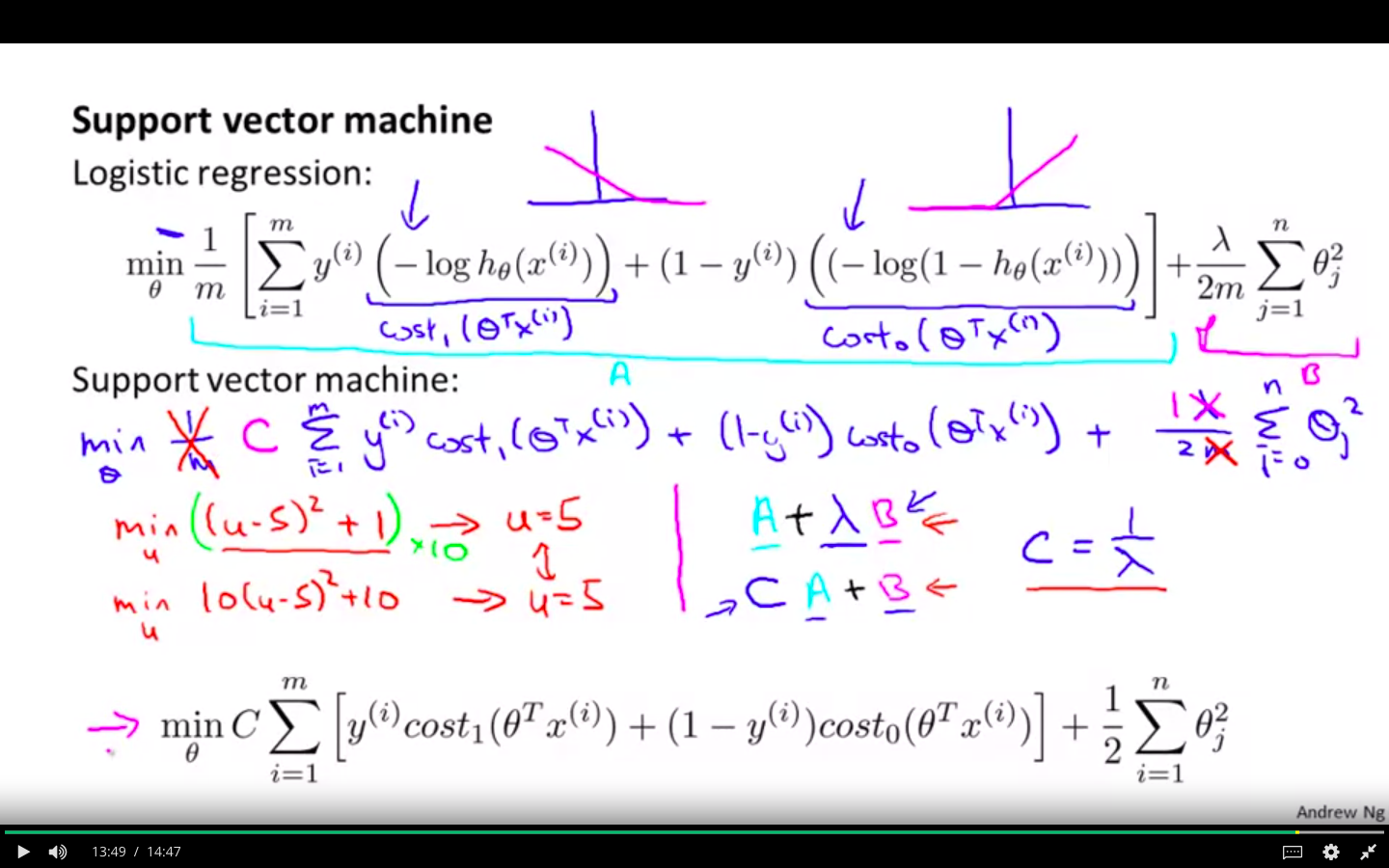
Support Vector Machine
- Modified hypothesis of Logistic Regression

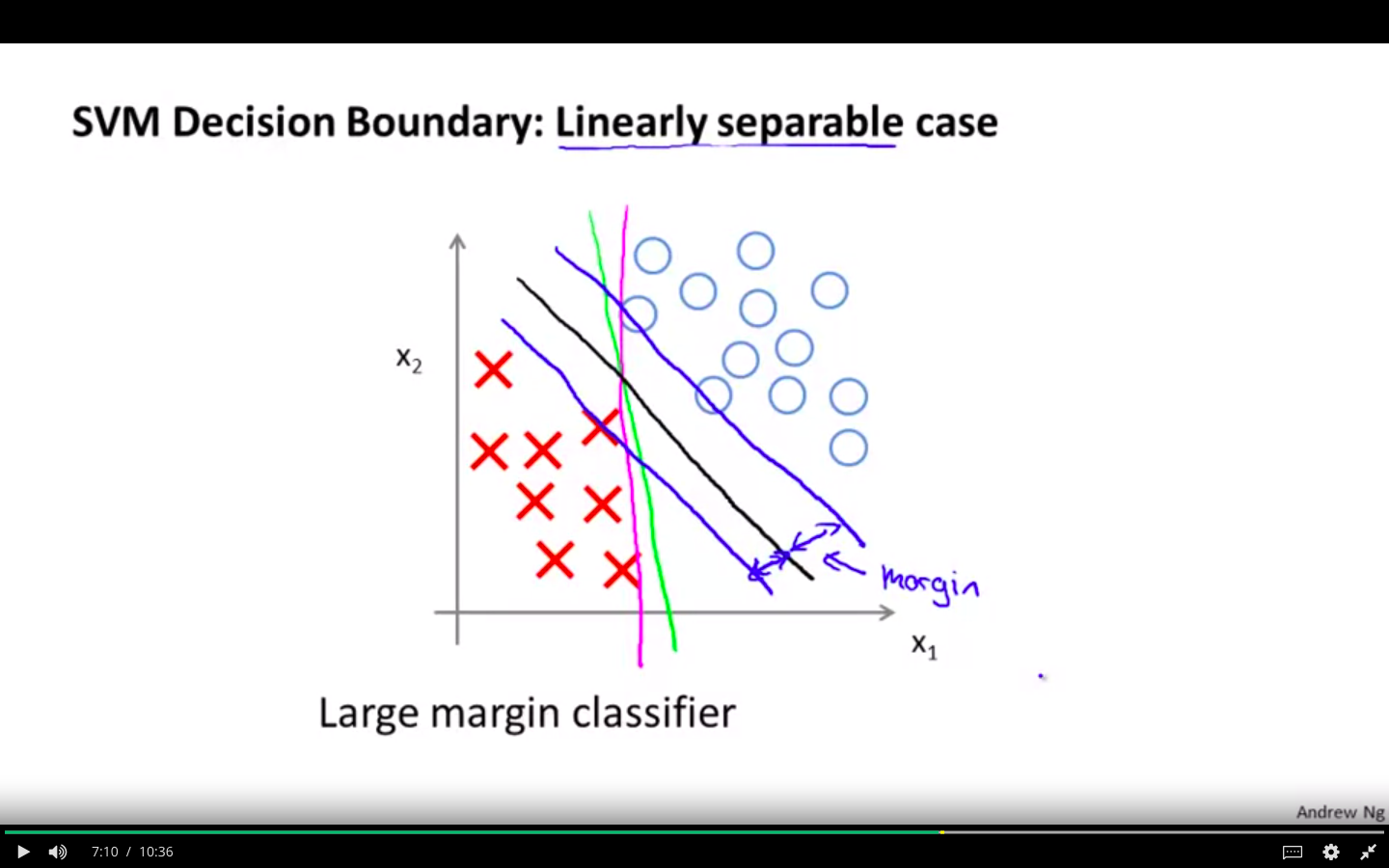
Large Margin Intuition
-
Concept
-
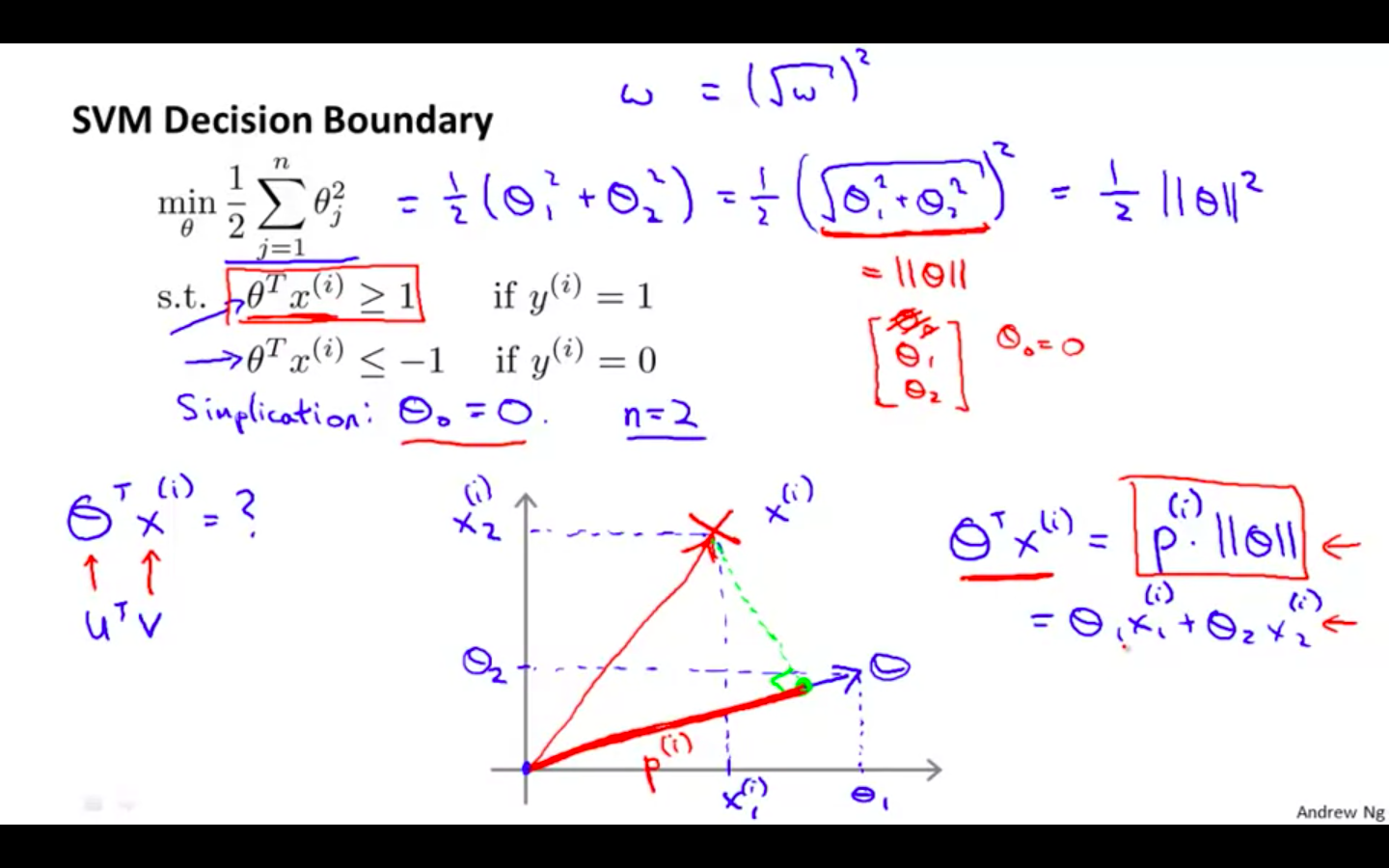
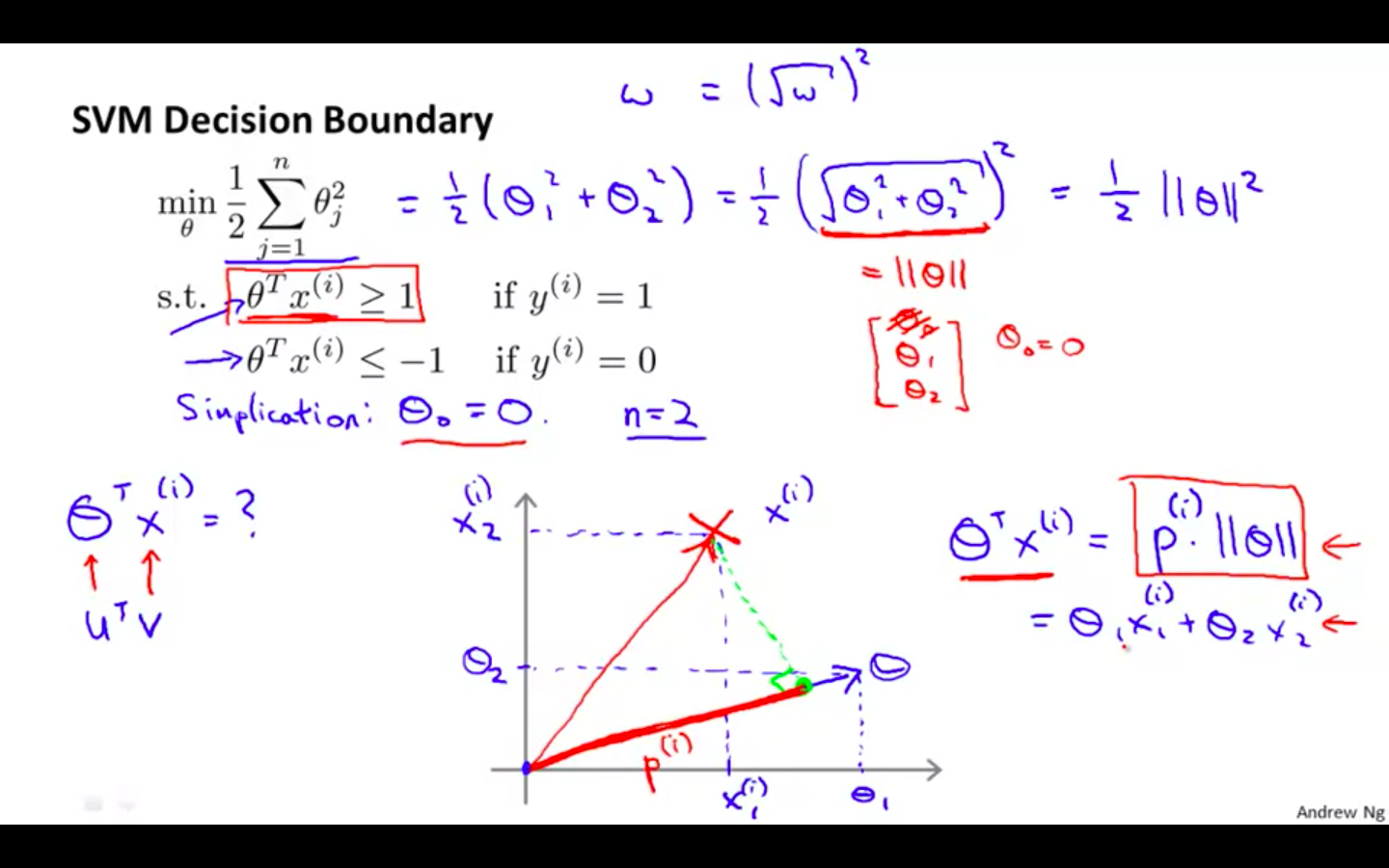
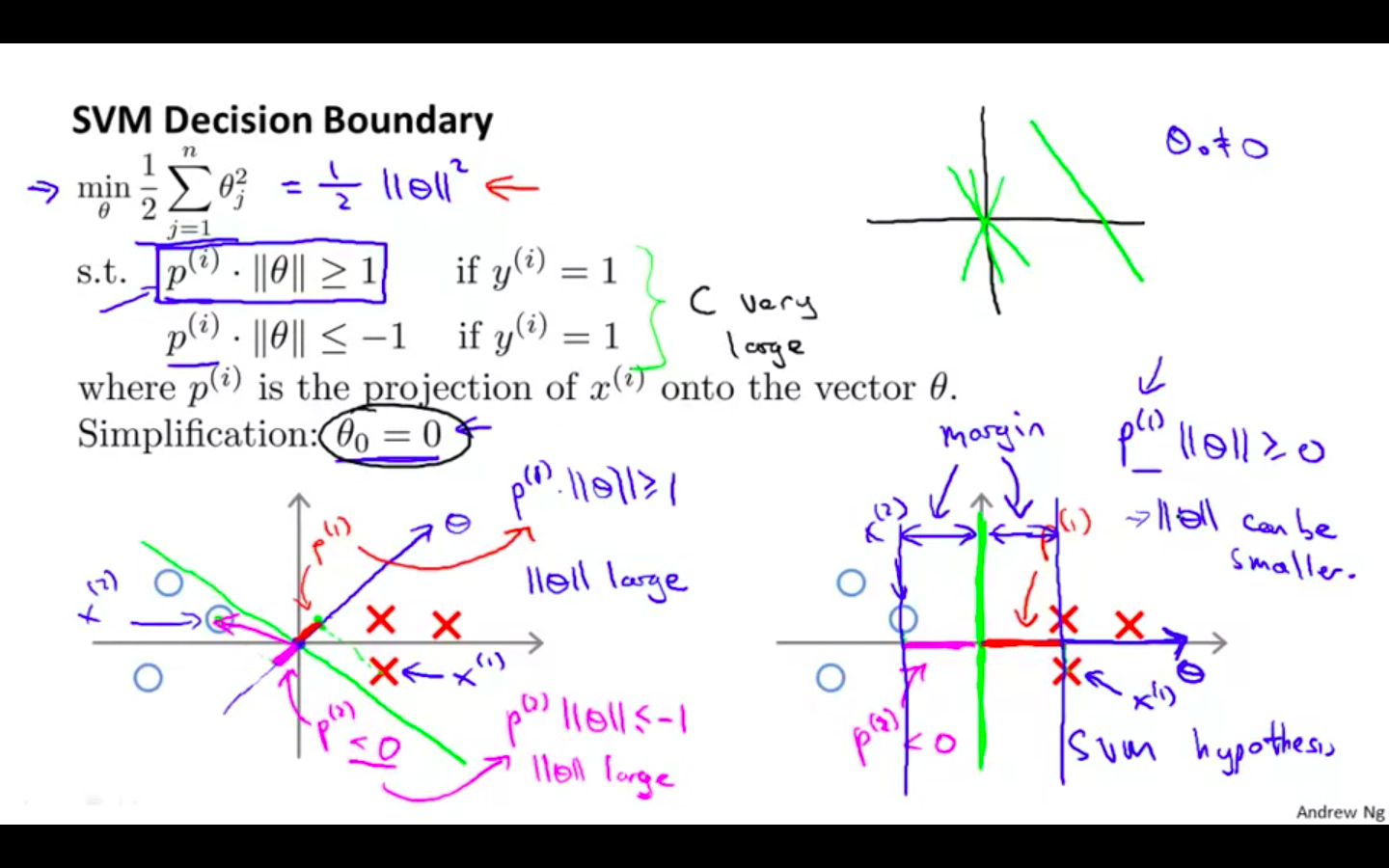
SVM Decision Boundary
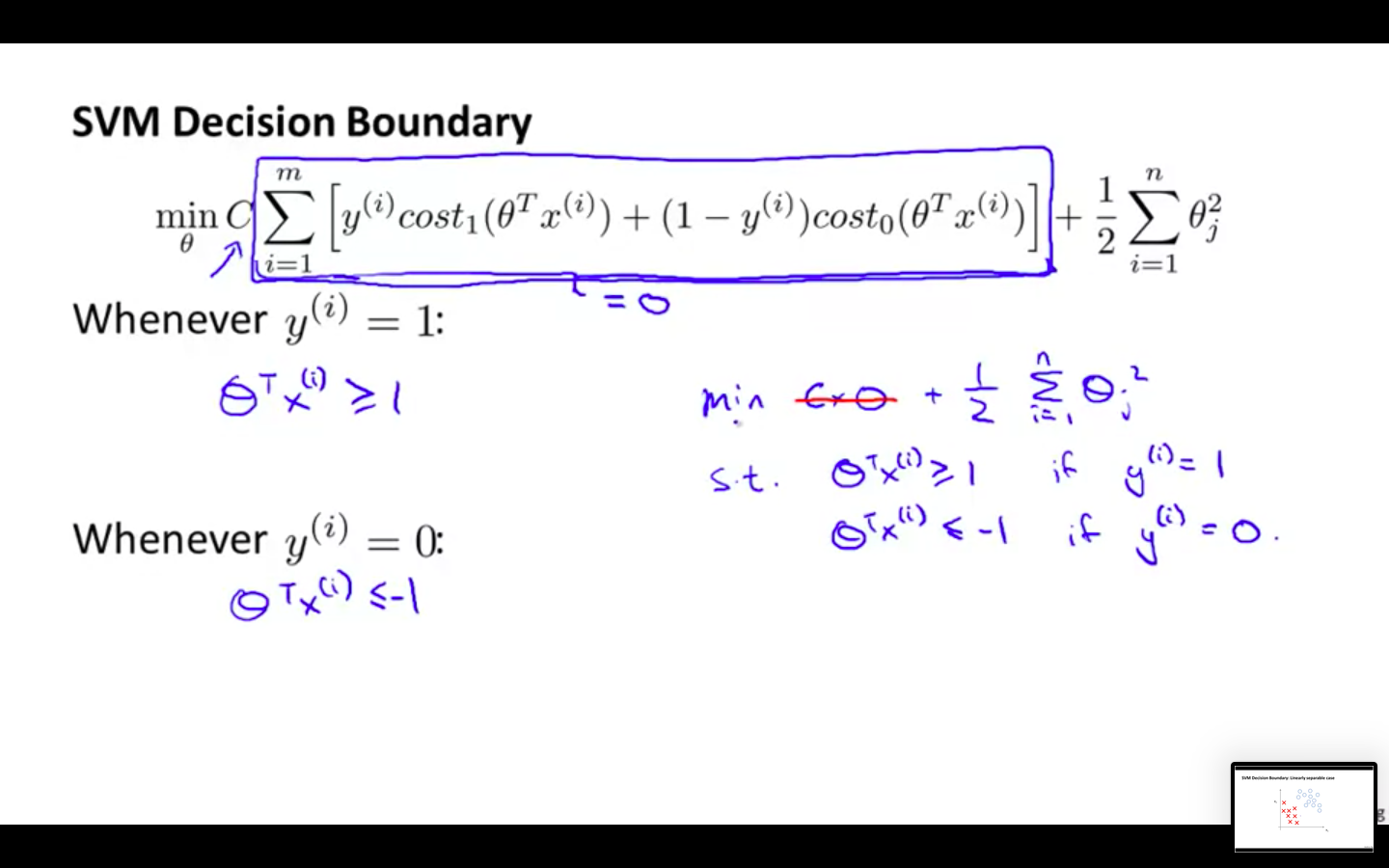
-
SVM creates a decision boundary in a way that there is some space between the samples and decision boundary
-
That space is called as margin
-
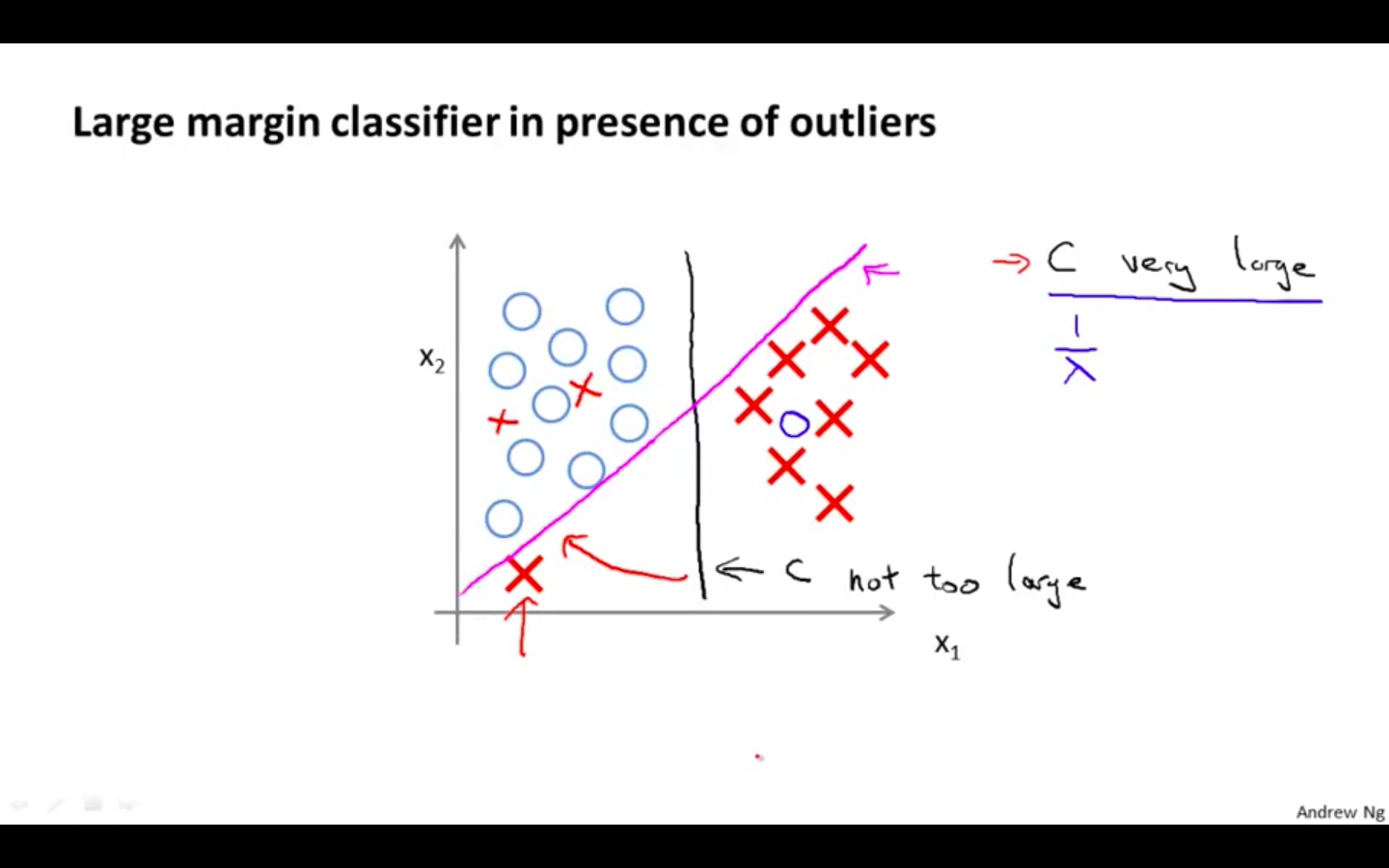
If C is too large the decision boundary will identical to magenta line
-
If C is not to large then the decision boundary will be identical to black line
-
Mathematics Behind Large Margin Classification
-
Vector Inner Product
-
u → euclidean length of vector u - p → length of projection of v onto u
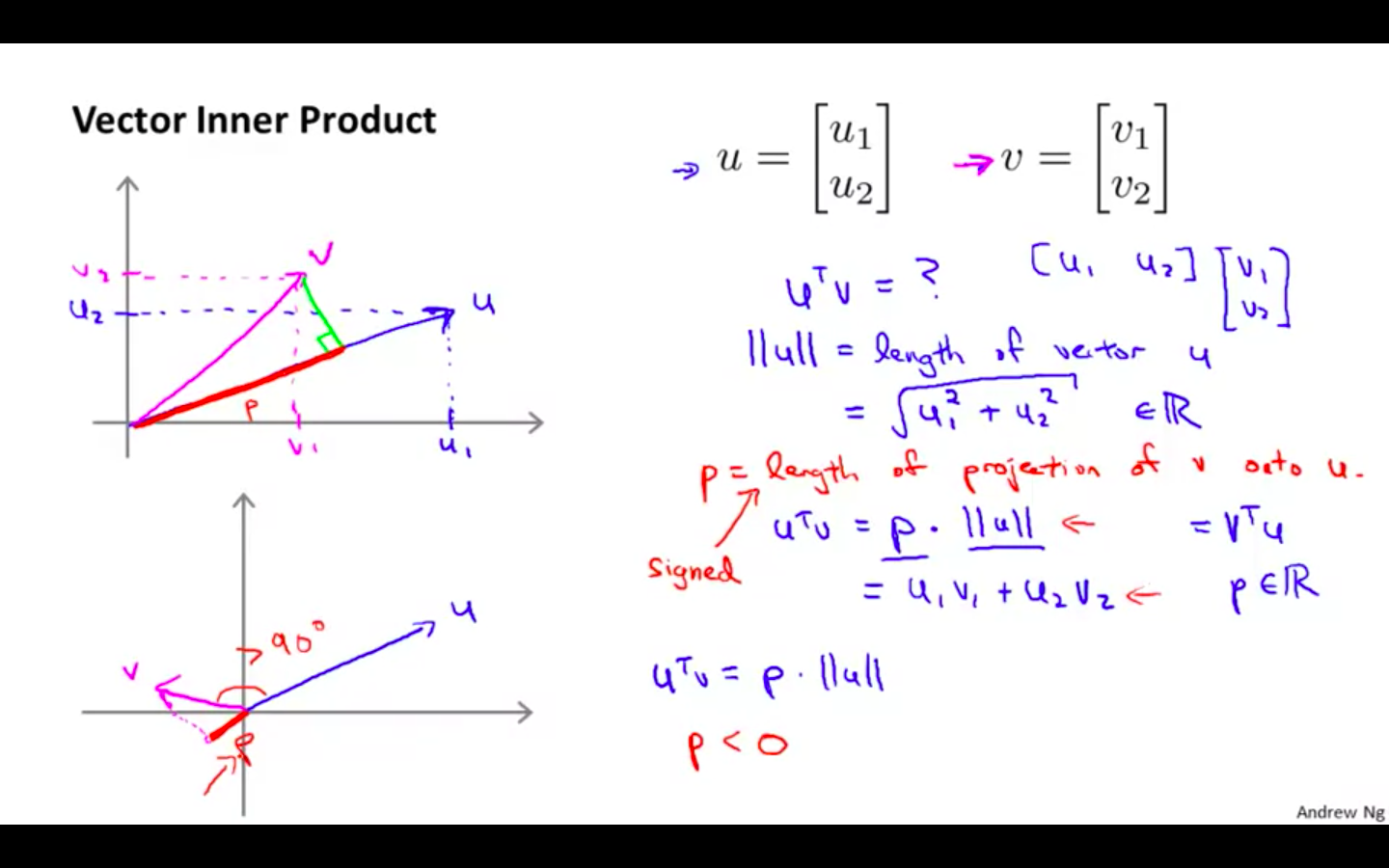
-
-
SVM Decision Boundary
Kernels
Kernels I
-
Non Linear Decision Boundary
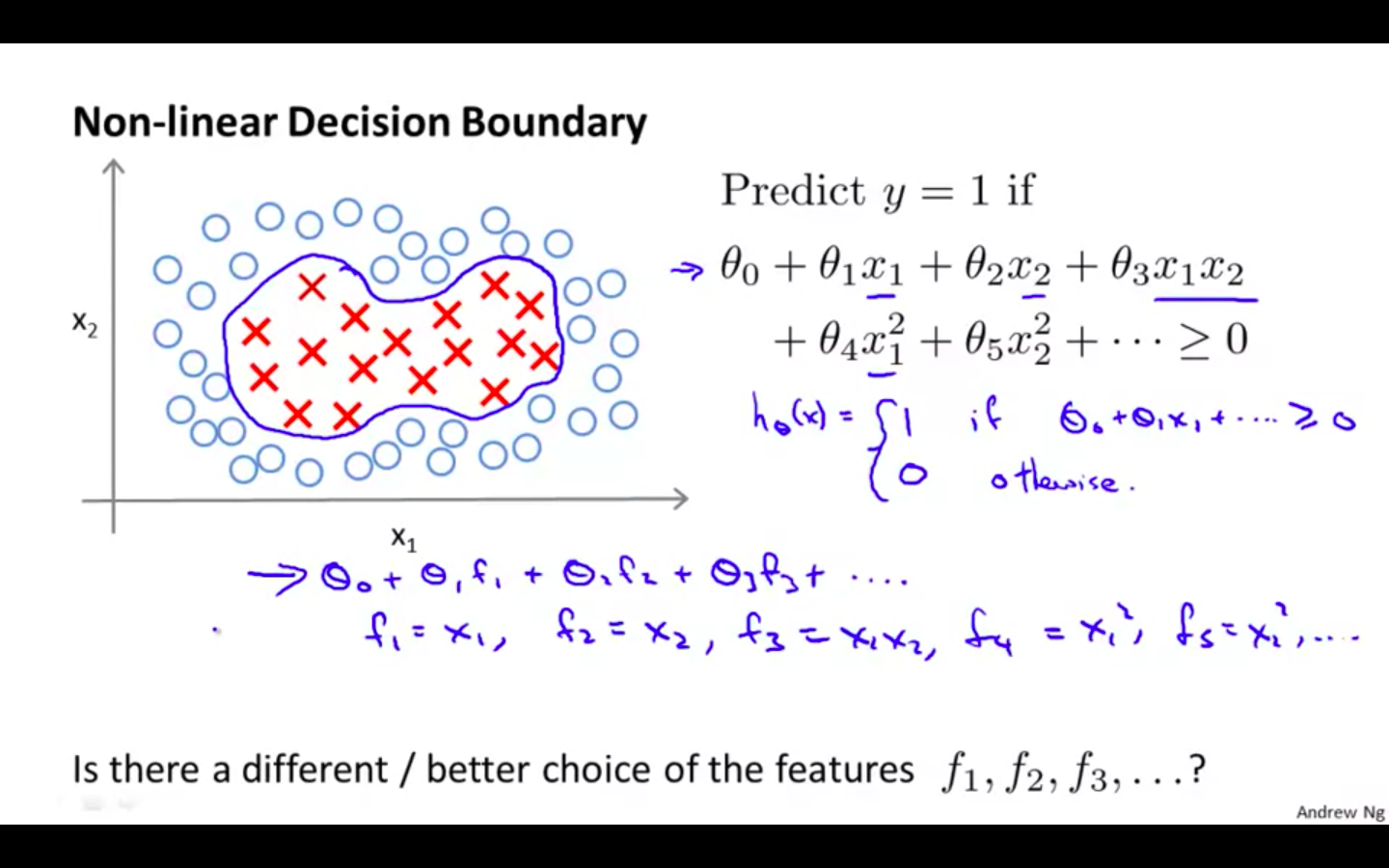
-
Kernels

-
Similarity
- Gaussian Kernel
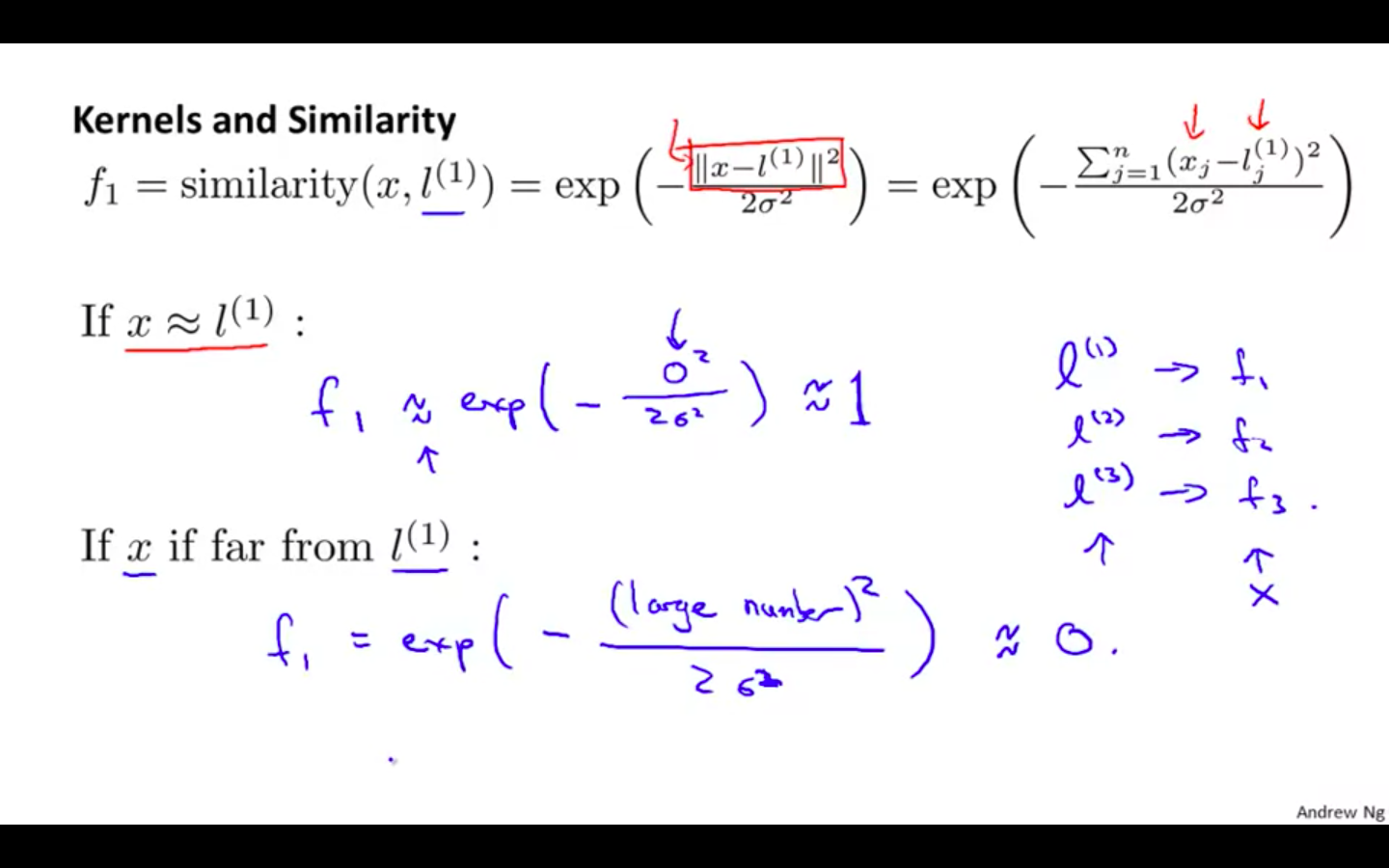
-
Exmaple
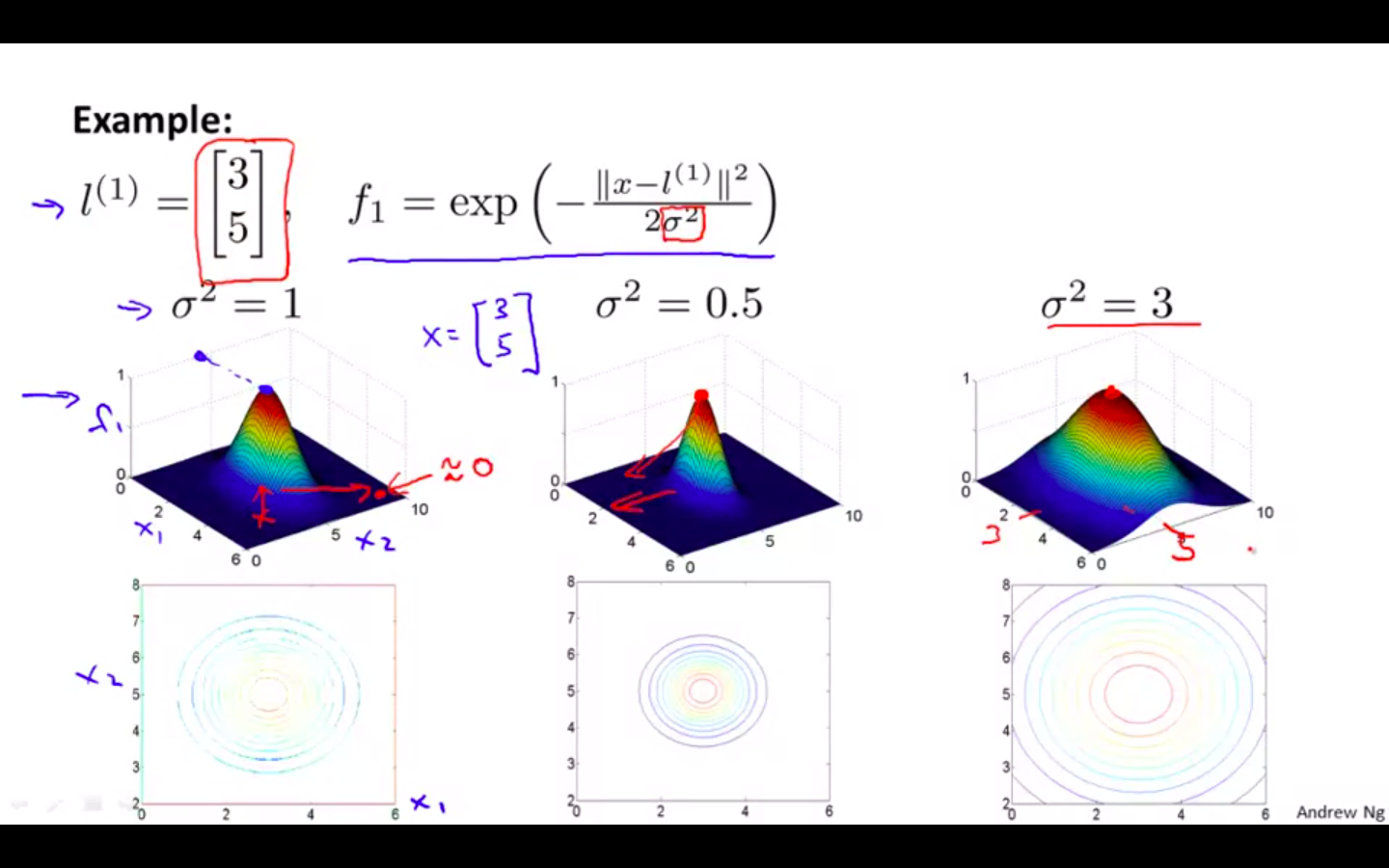
-
Concept
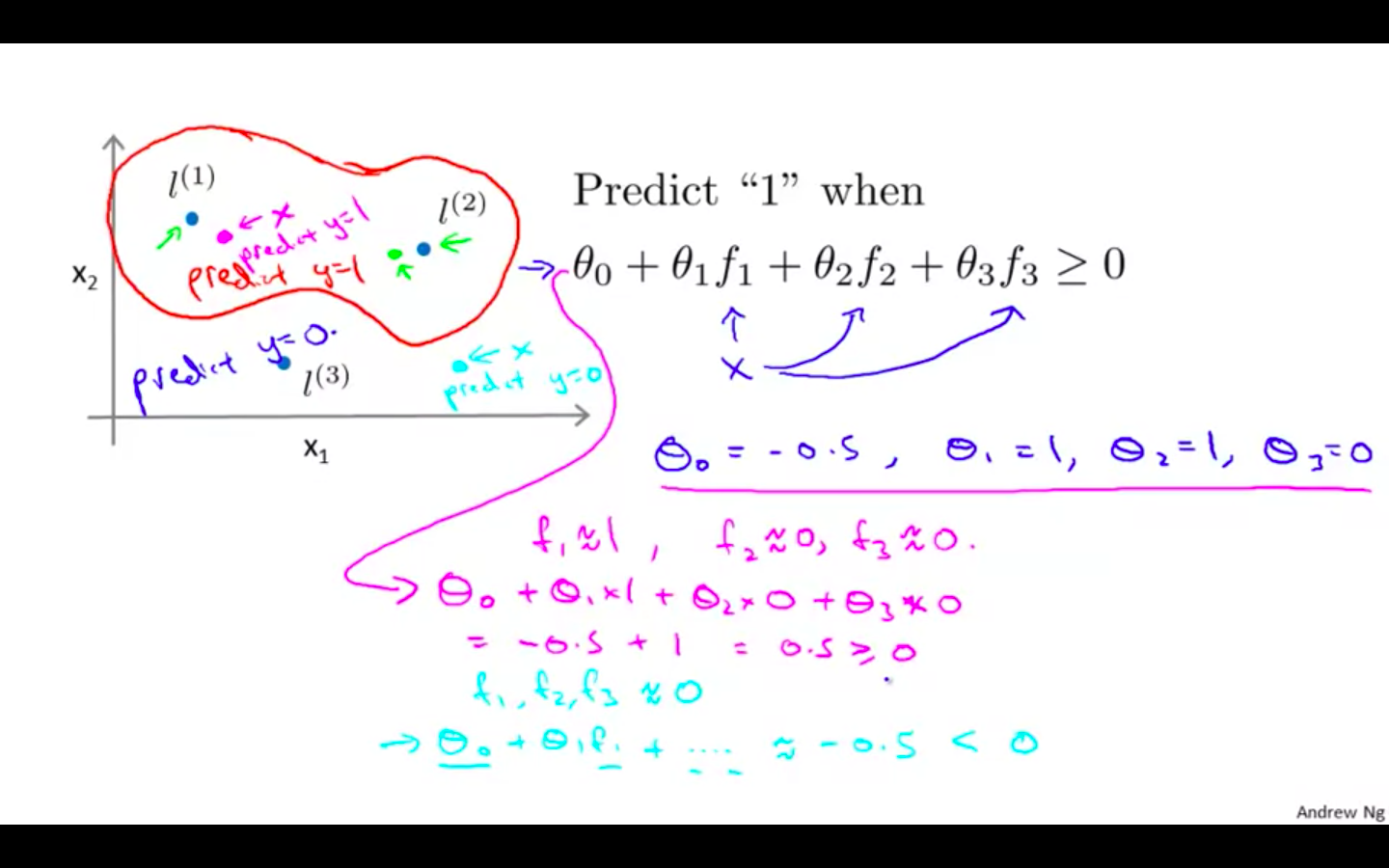
-
Kernels II
-
Choosing Landmarks
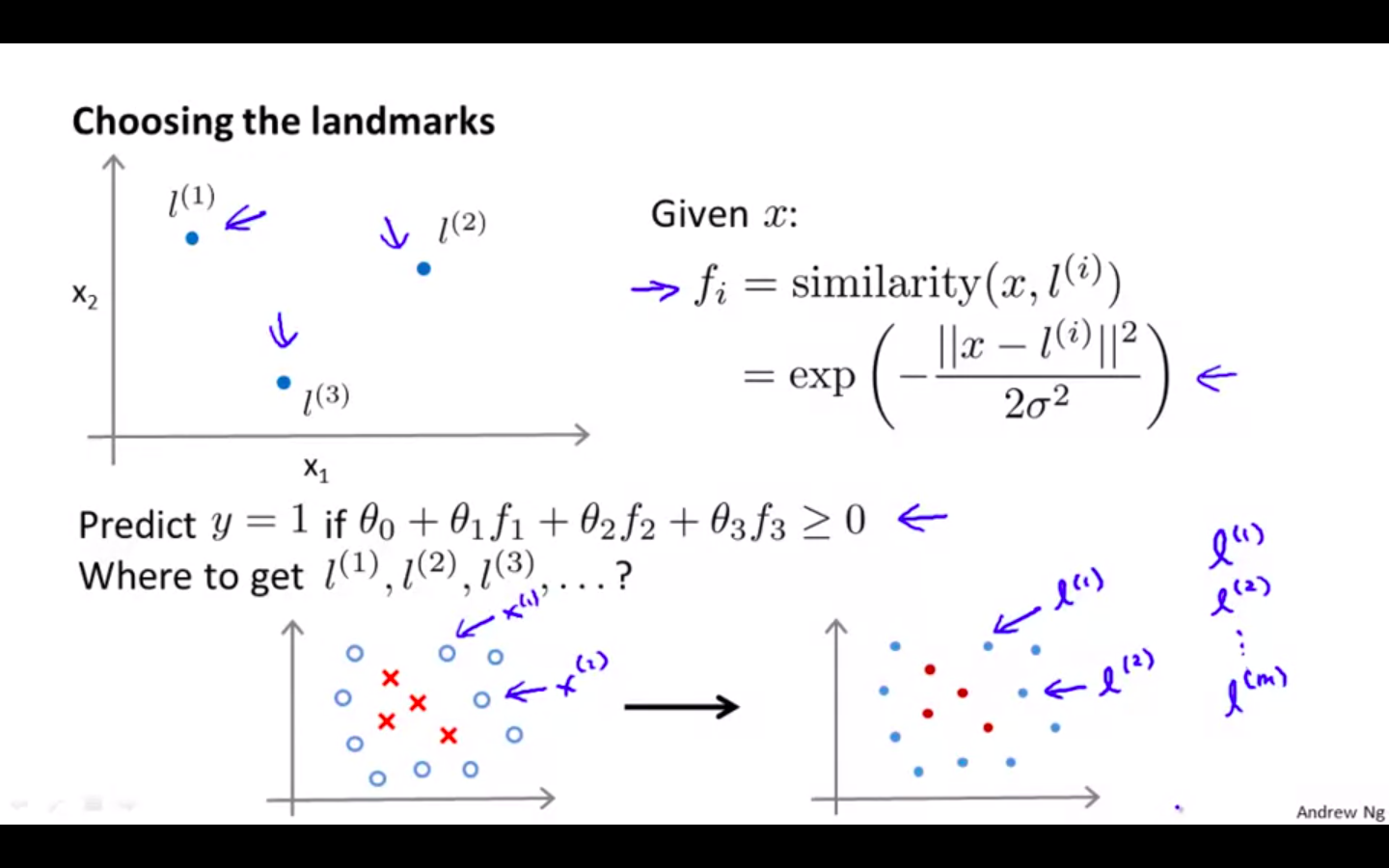
-
SVM with Kernels
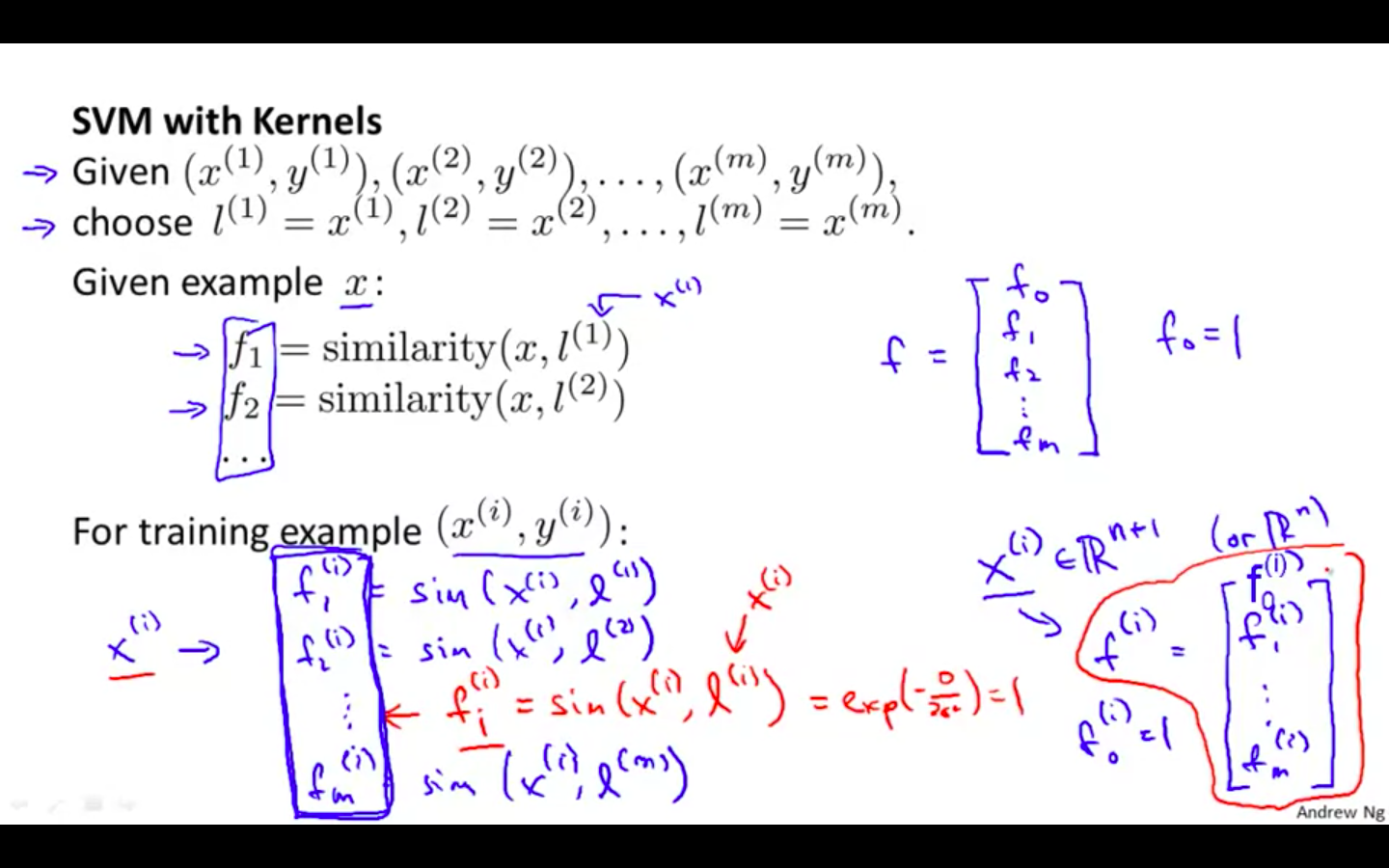
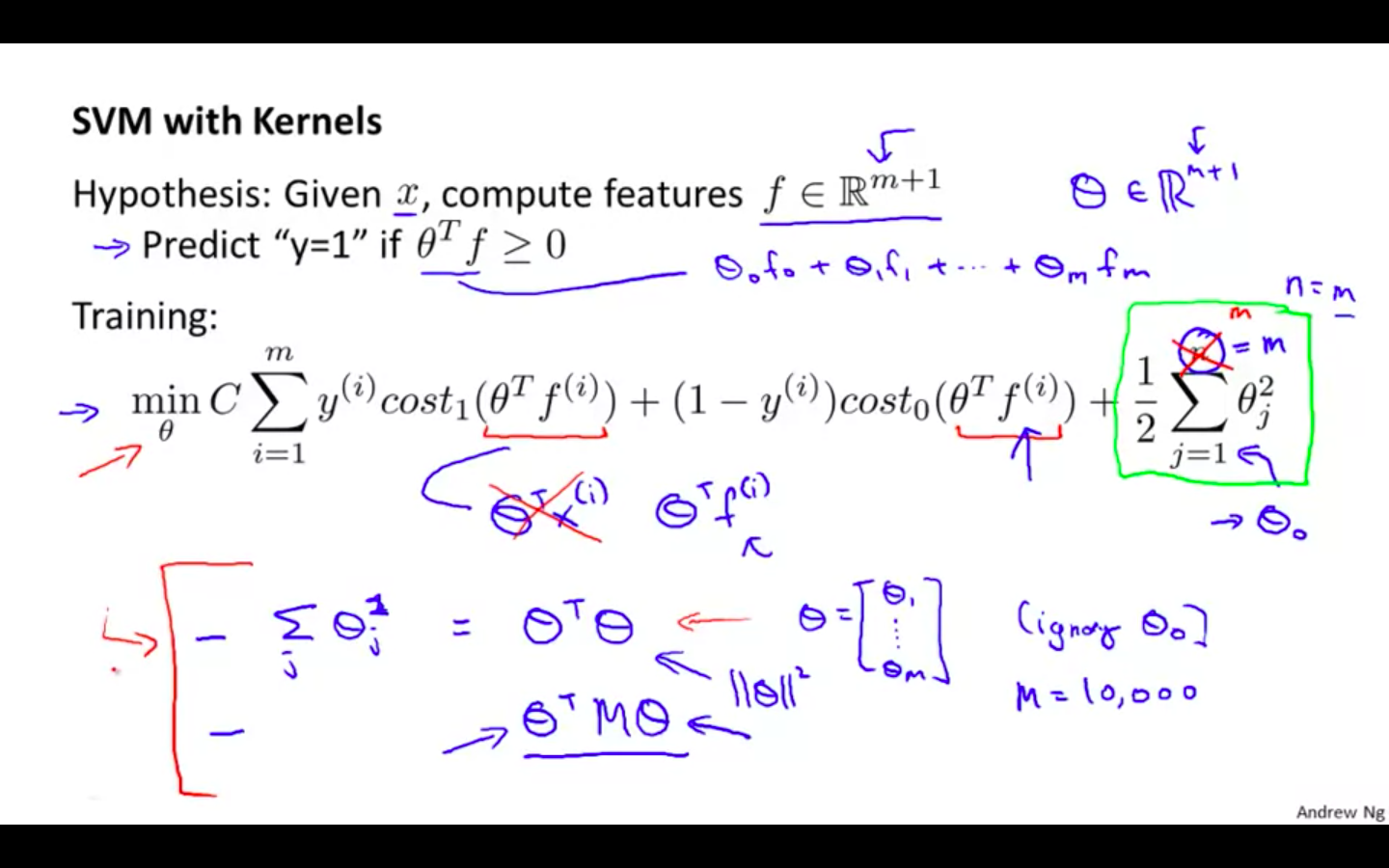
-
SVM Parameters
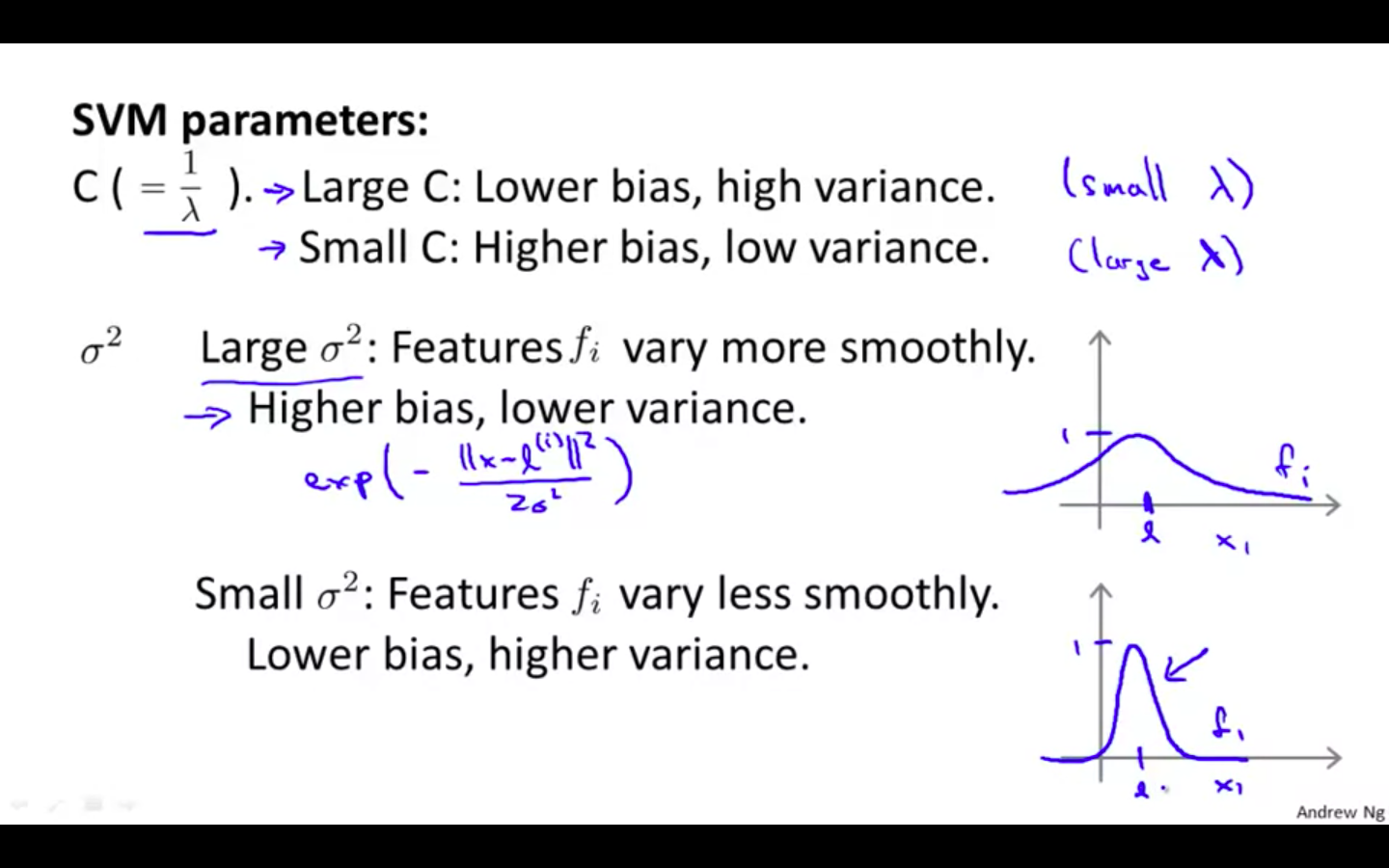
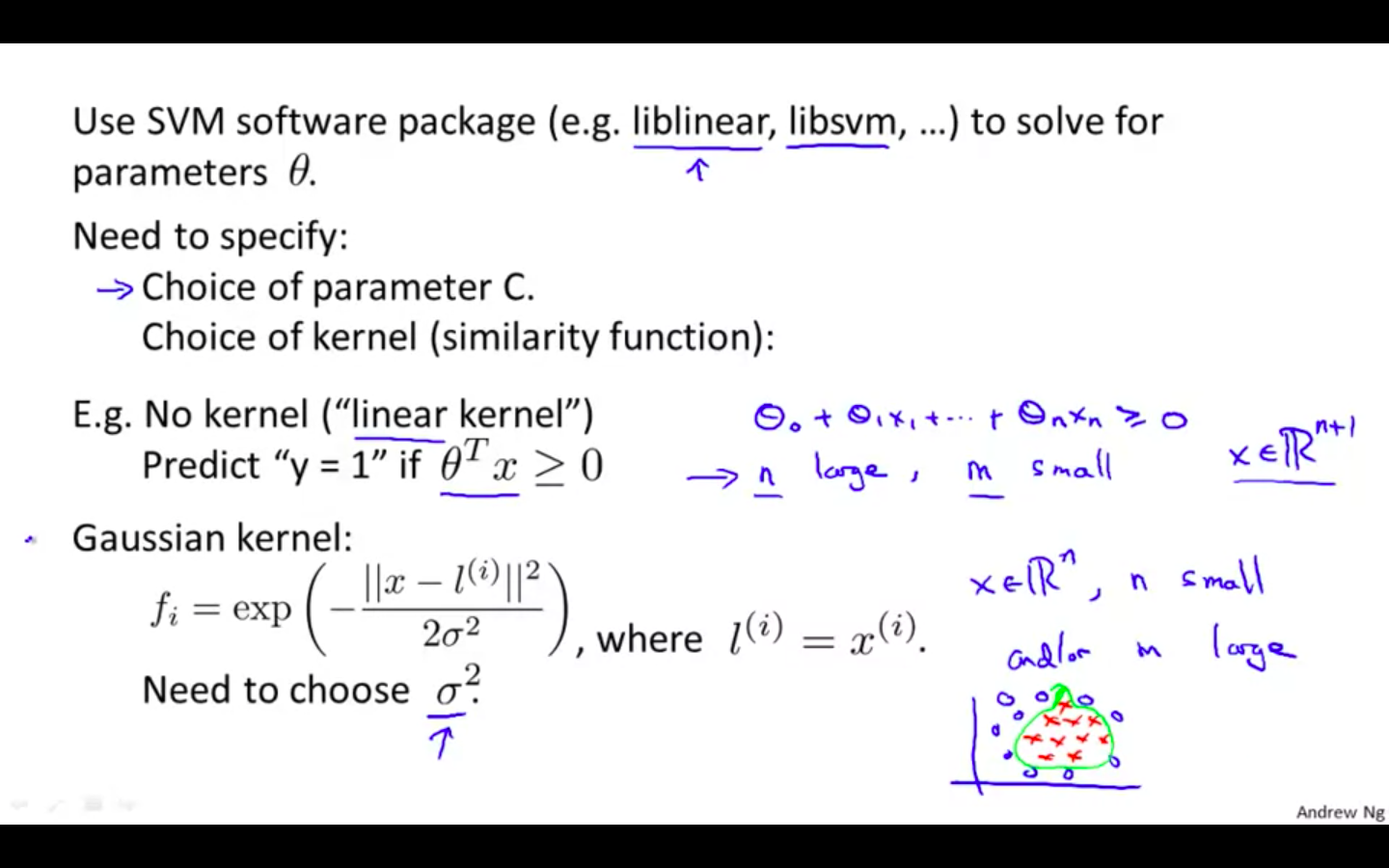
SVMs in Practice
Using An SVM
-
Overview
-
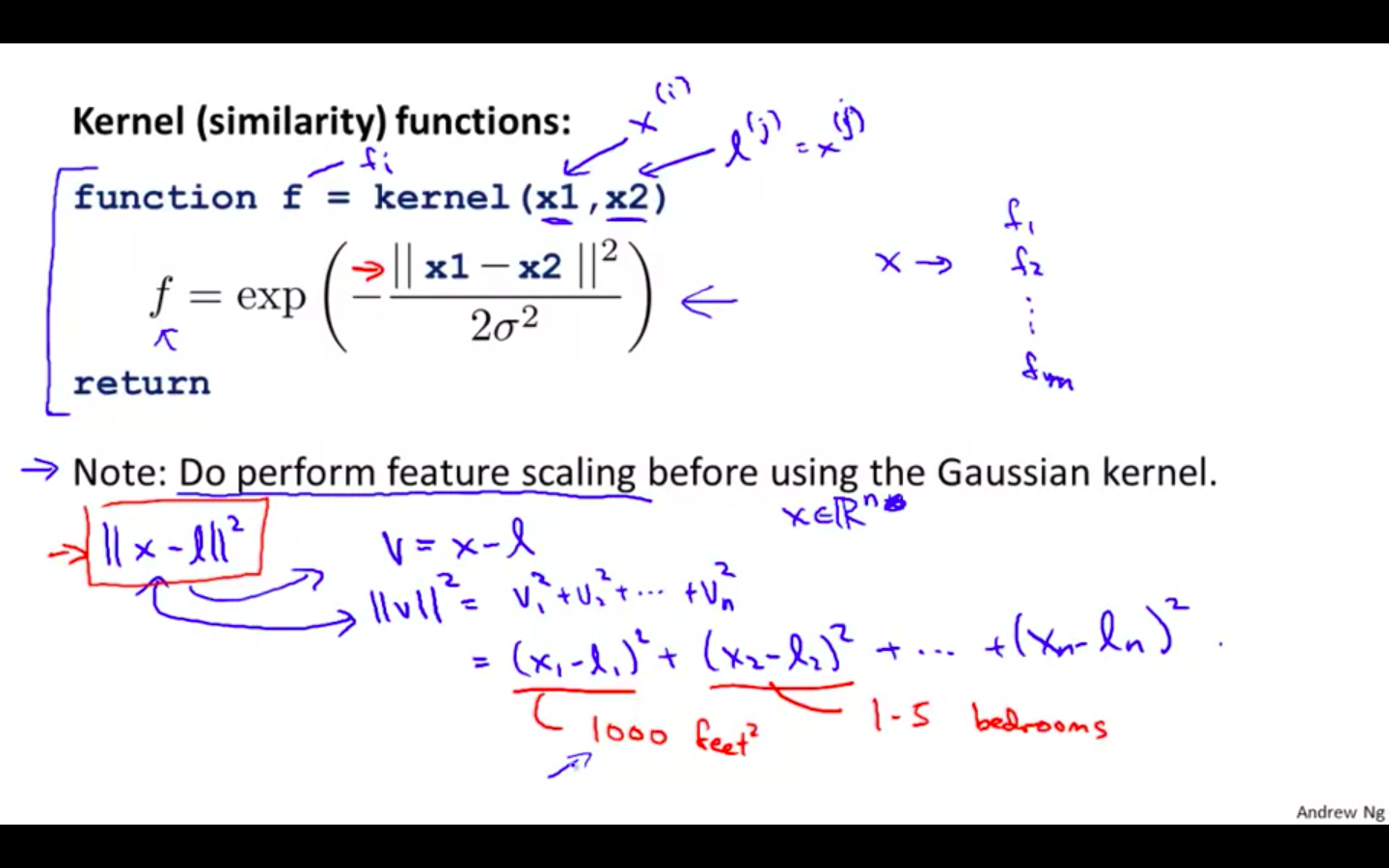
Octave Implementation
-
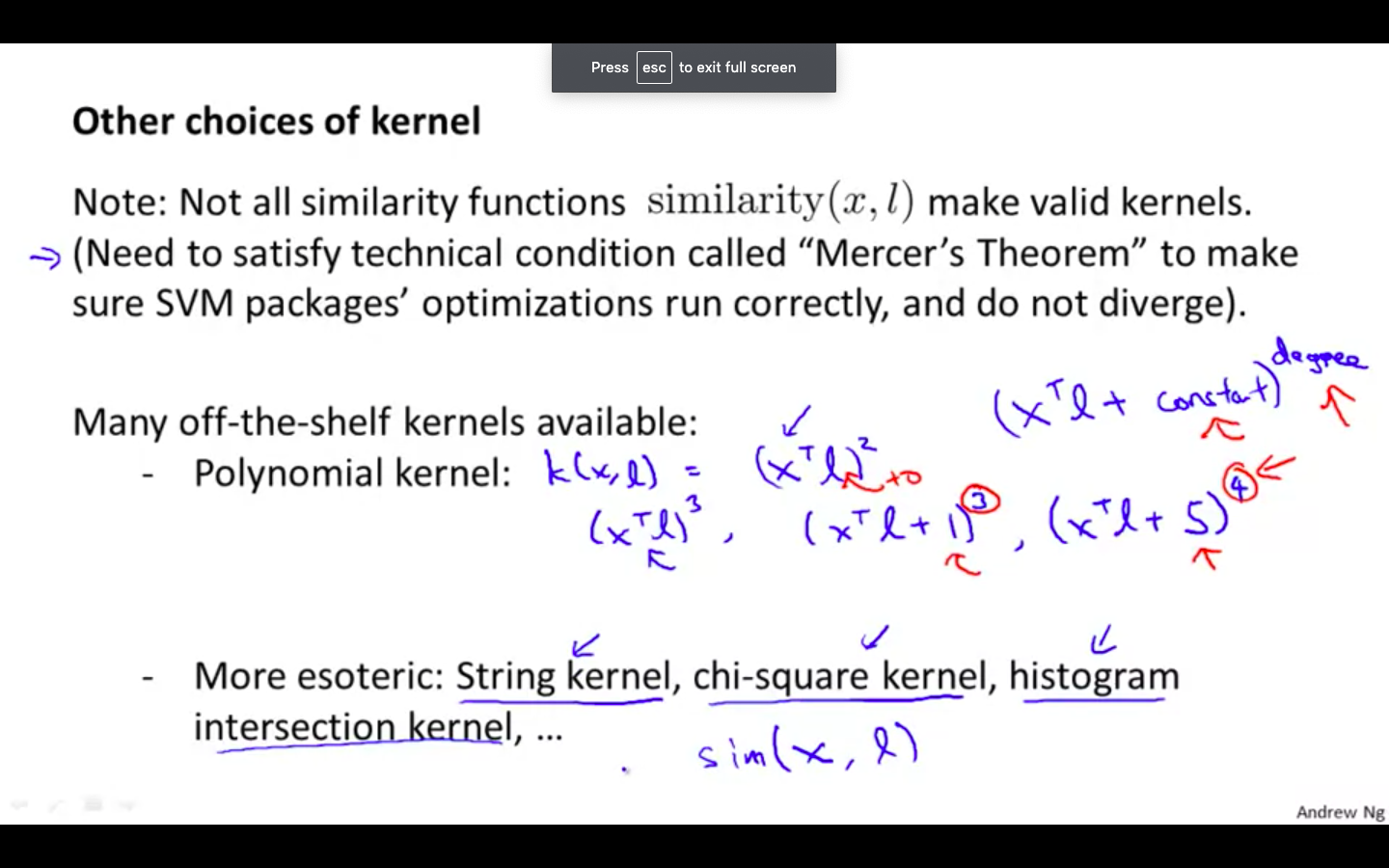
Other Kernels
-
Multi Class Classification
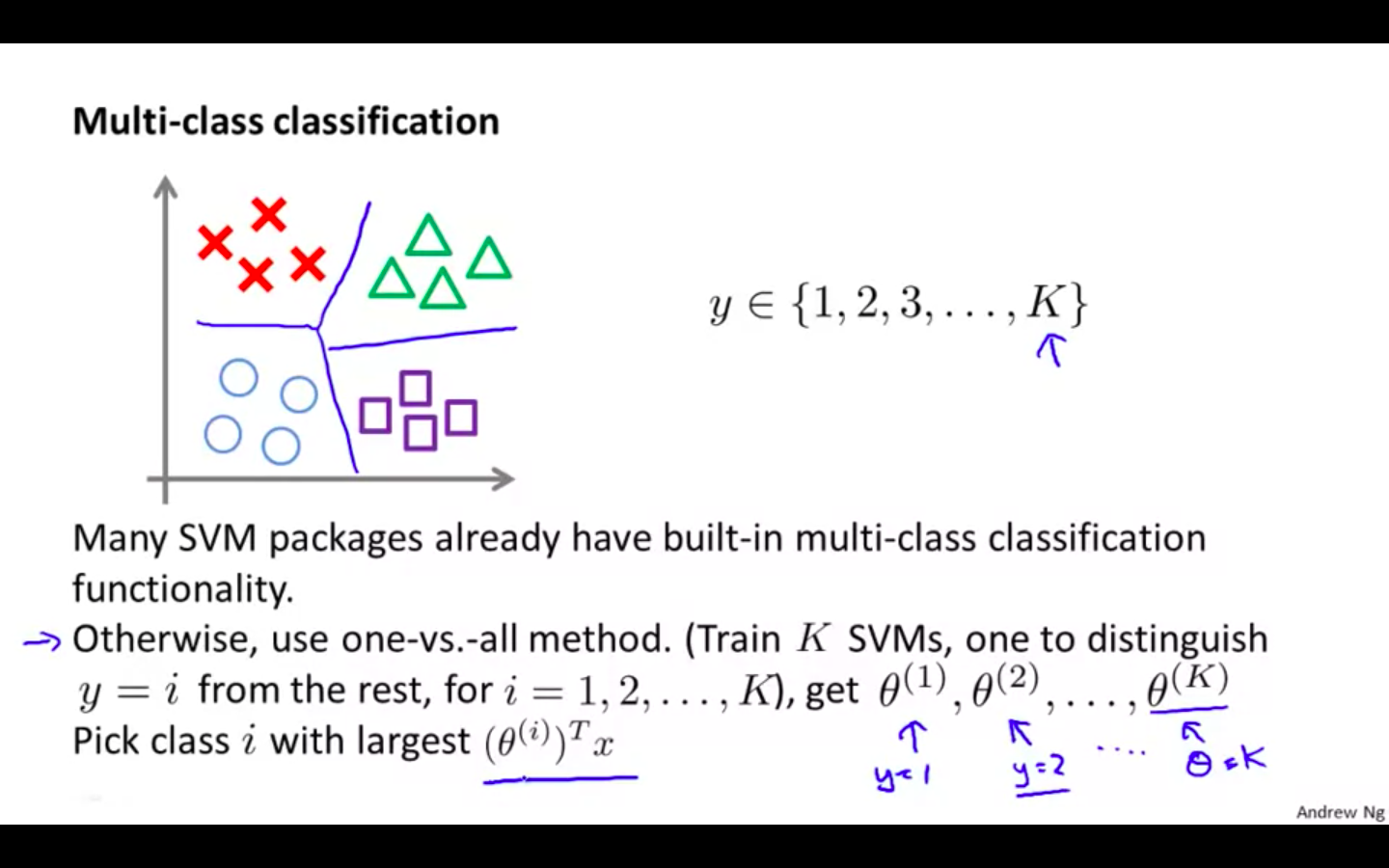
-
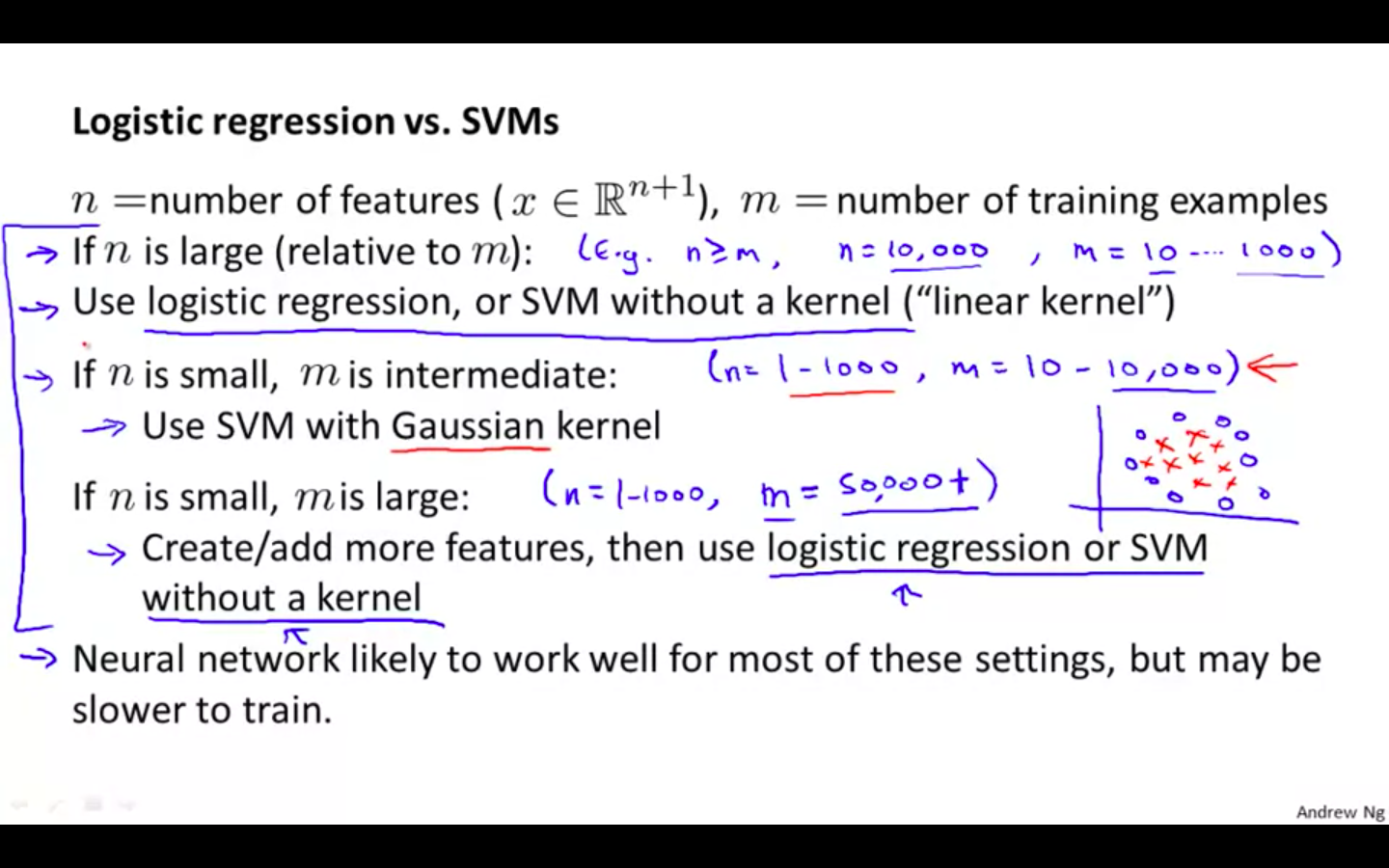
Logistic Regression VS Support Vector Machine