Machine Learning By Andew Ng - Week 8
Clustering
Unsupervised Learning: Introduction
-
The data in the supervised learning problems comes with labels
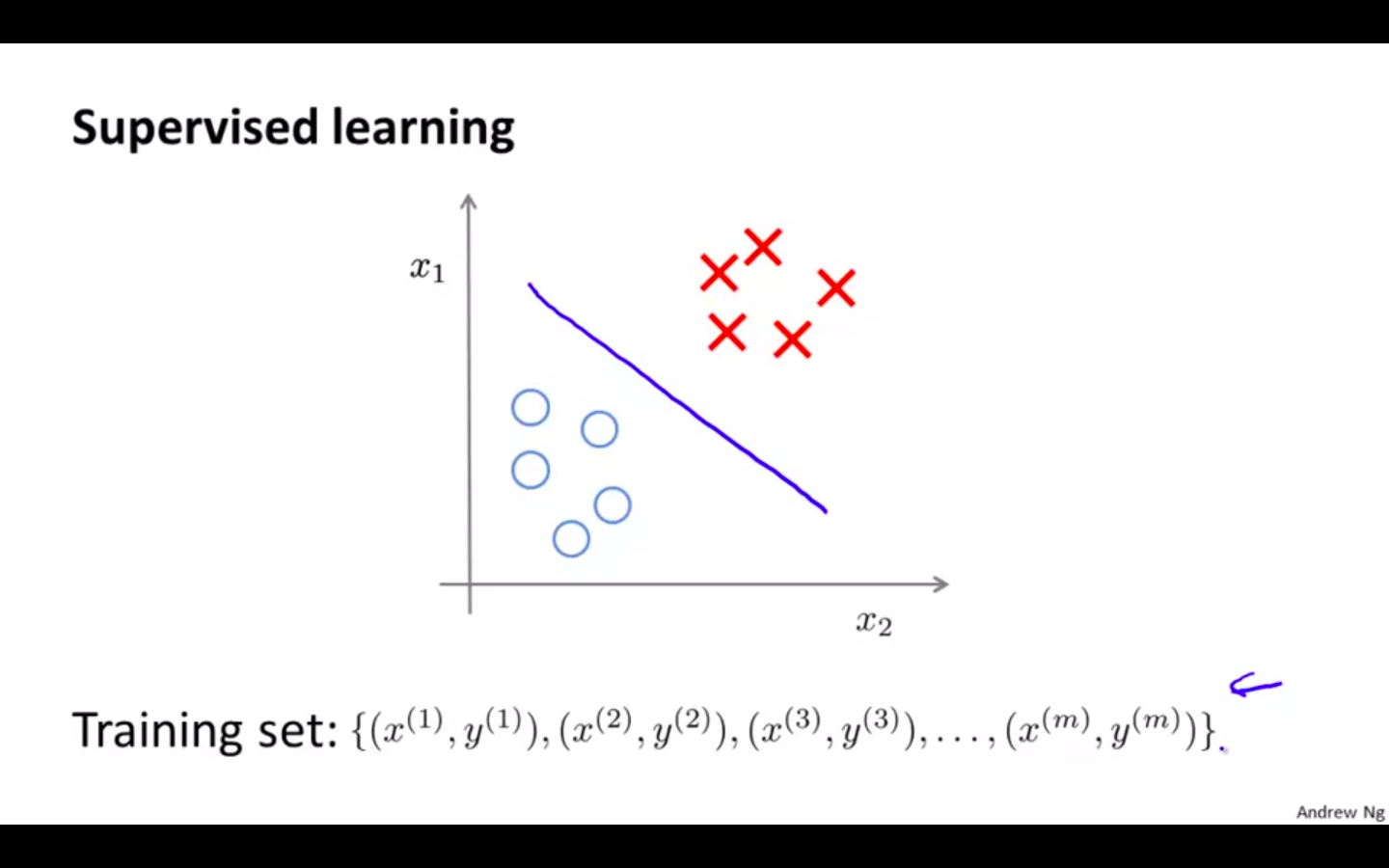
-
The data in the unsupervised learning problems doesn’t come with the labels
-
Unsupervised learning algorithms are meant to find the structure in the dataset
-
Clustering algorithm is used find groups of data point on the dataset
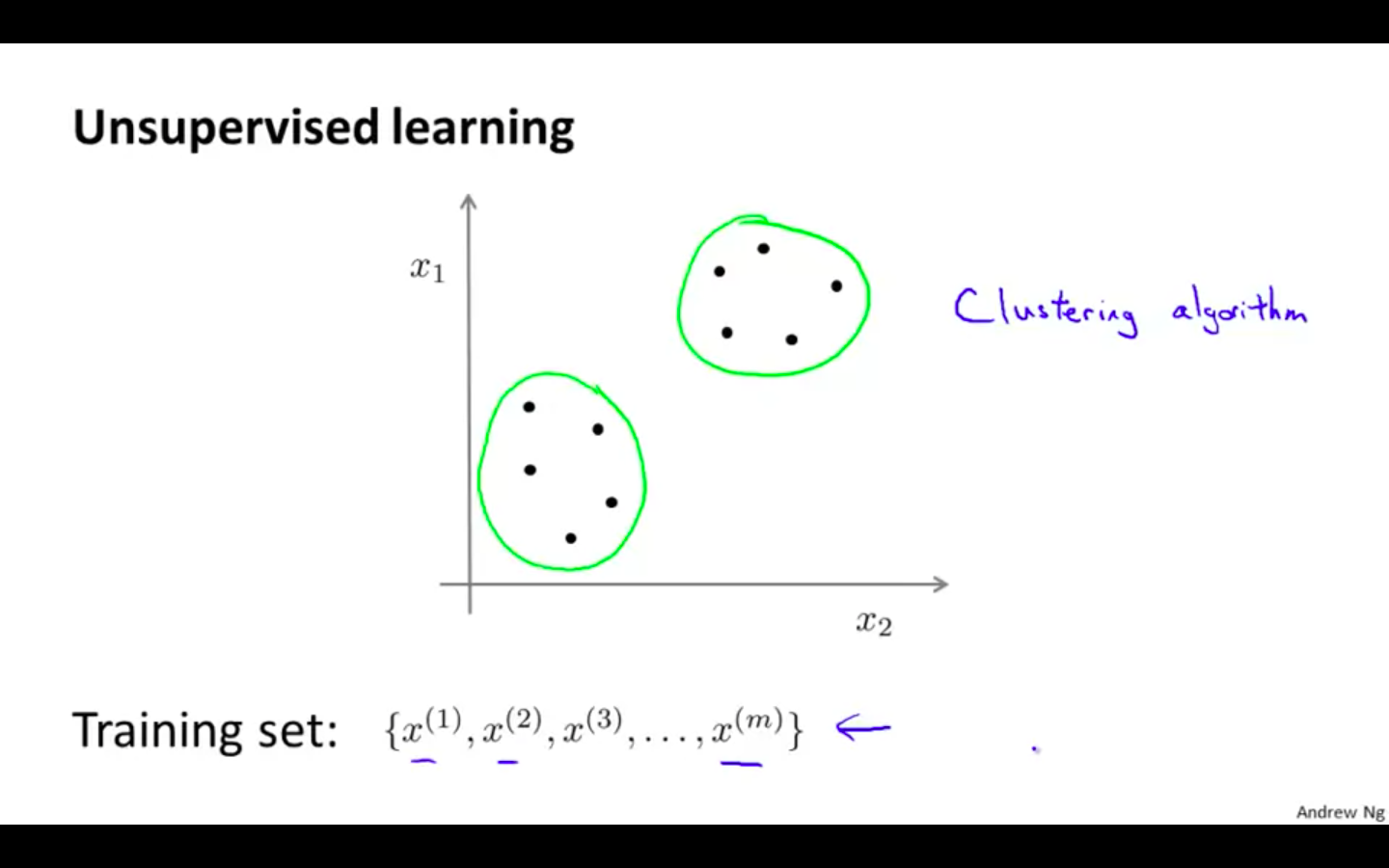
K-Means Algorithm
-
This is a Clustering Algorithm
-
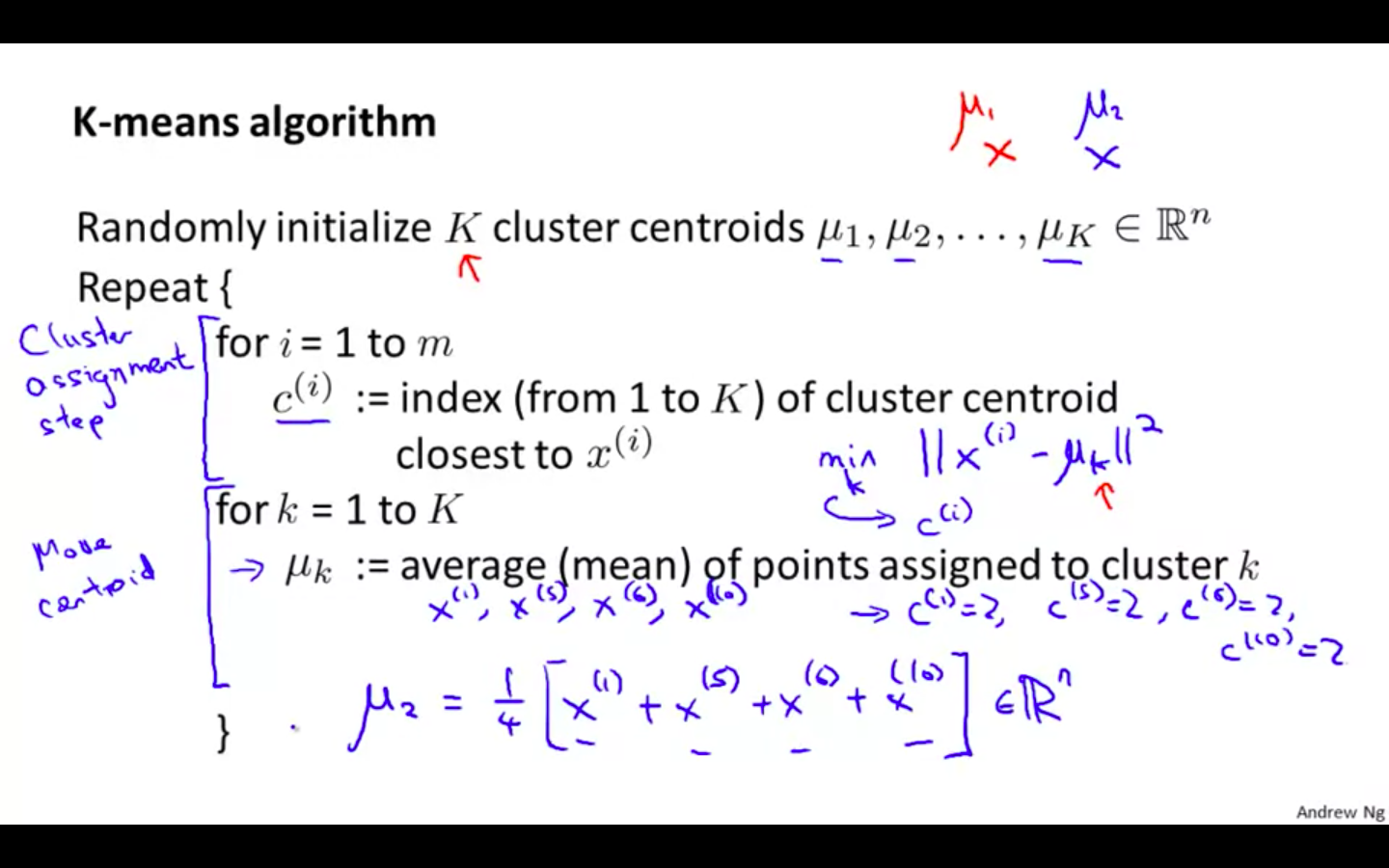
Steps
-
Cluster Centroids
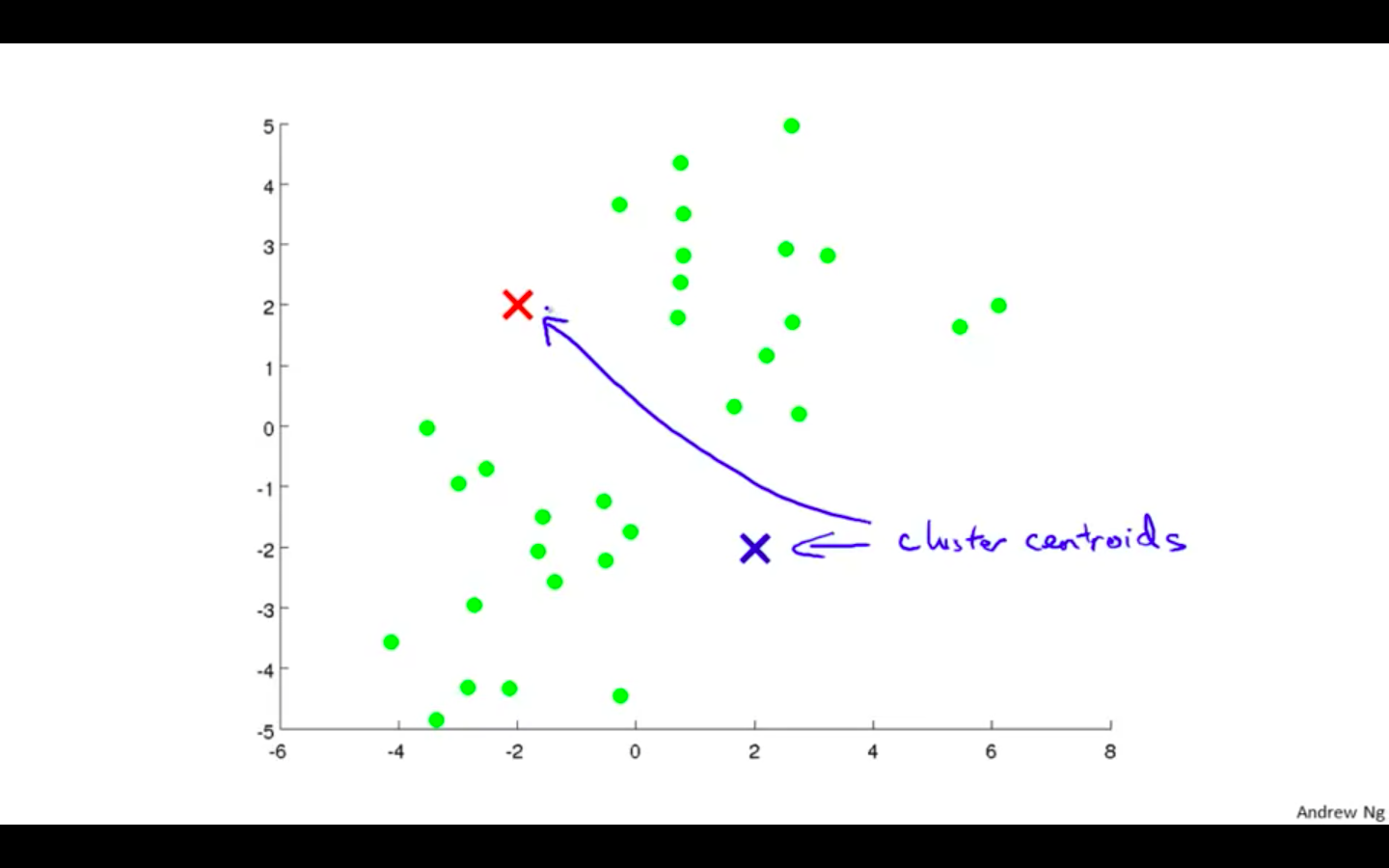
-
Random Initialisation
-
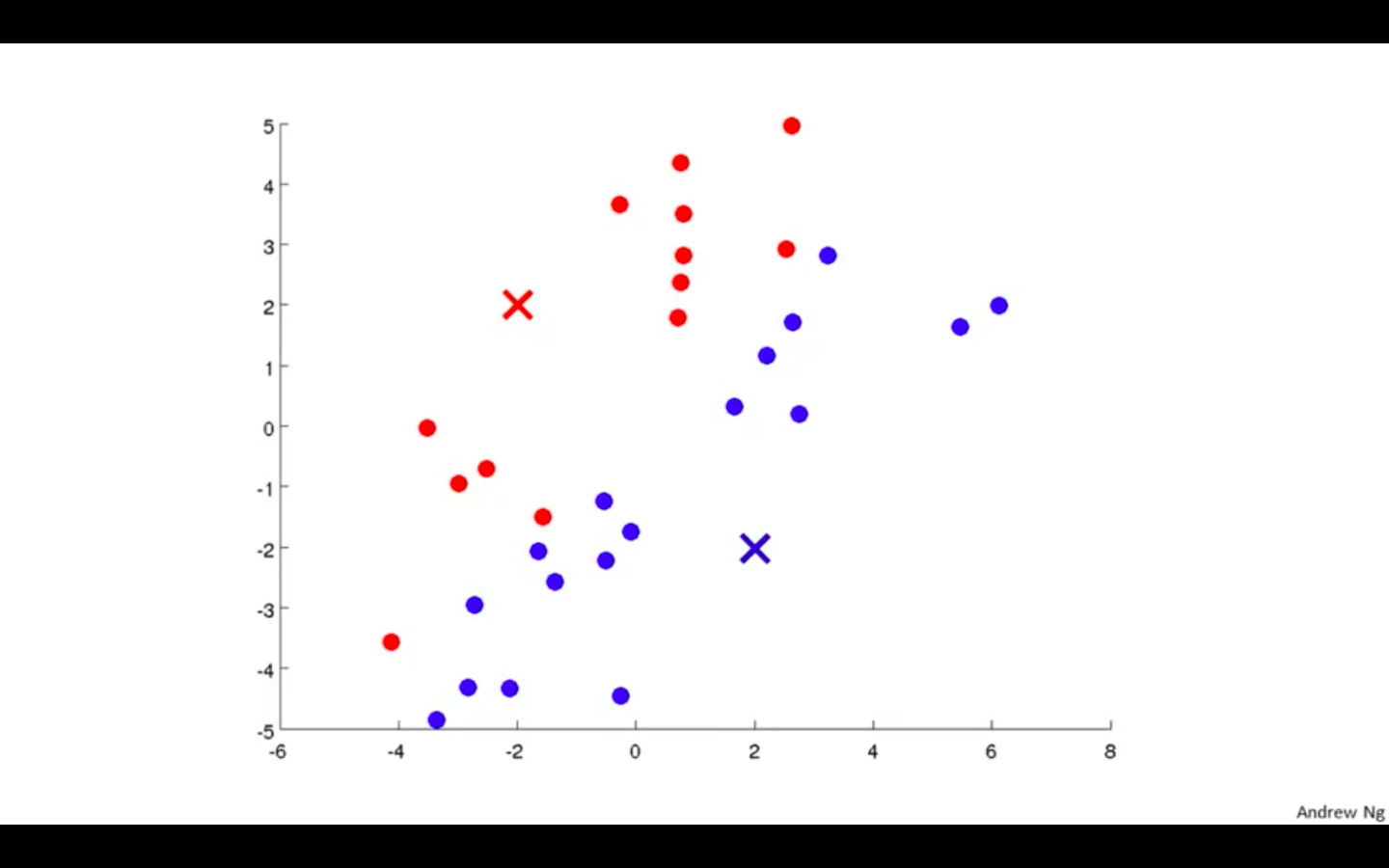
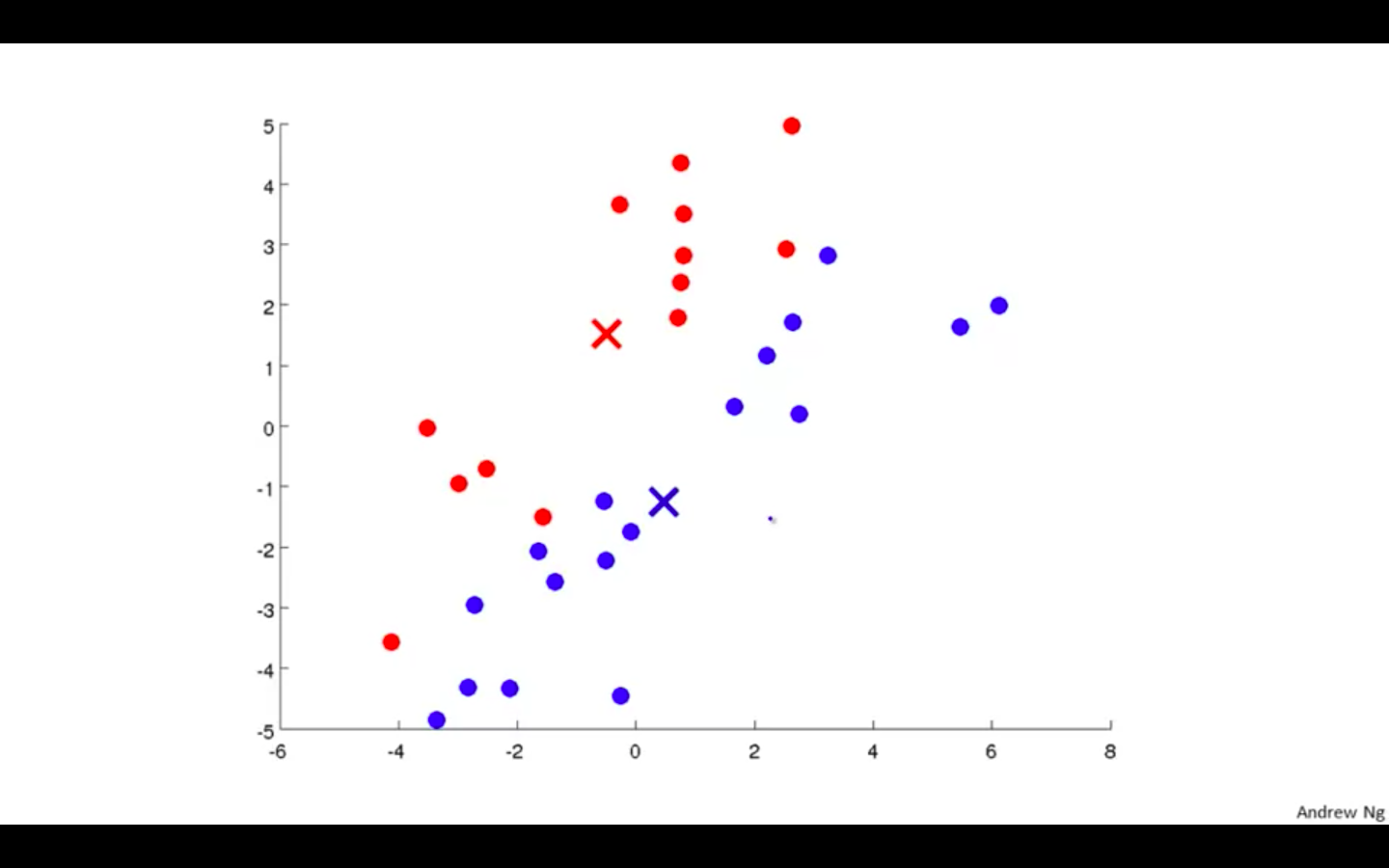
Mark a new cluster according to the points nearer to the centroids
-
Move Centroids to the average of new cluster
-
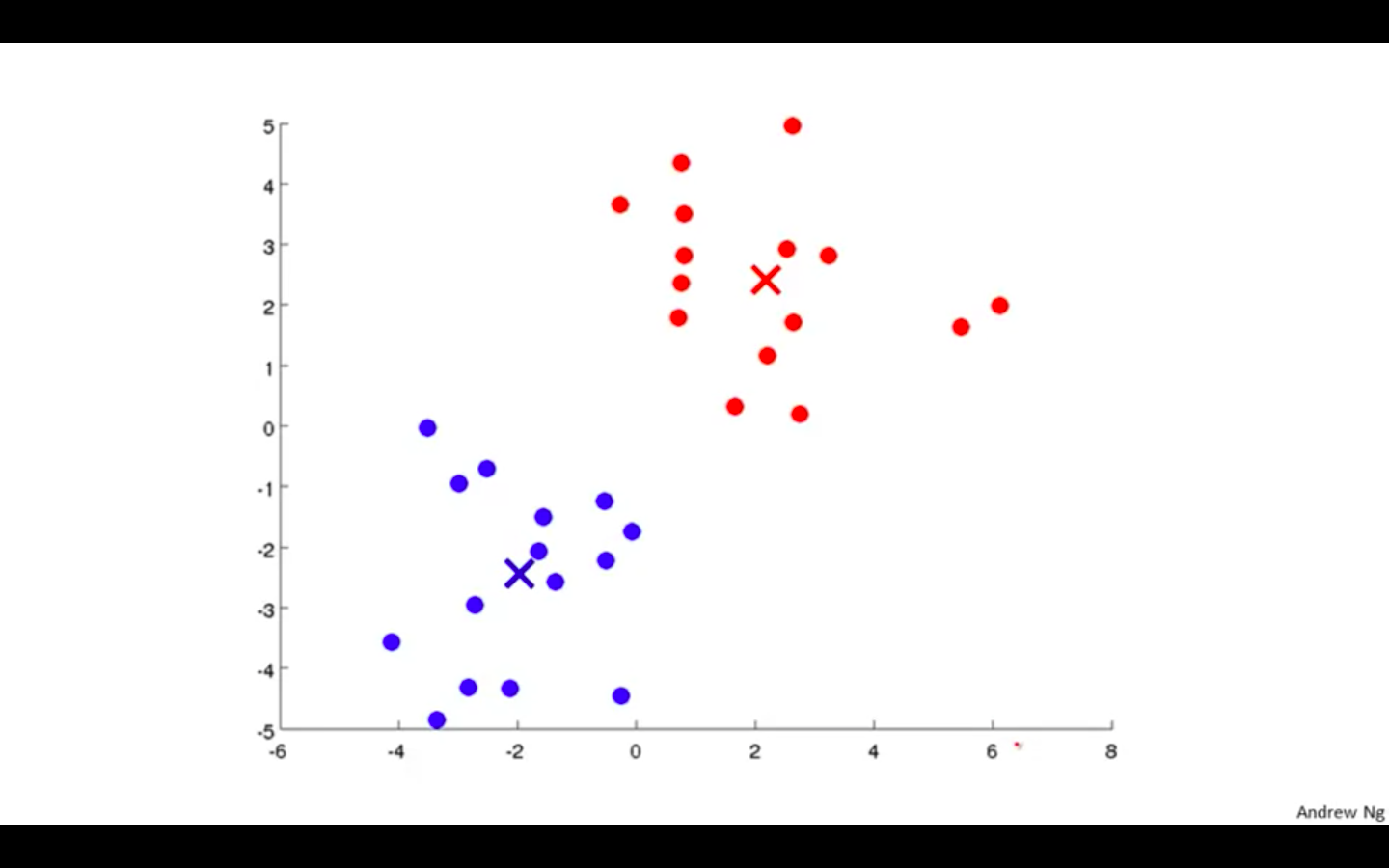
Repeat until the centroid doesn’t change
-
-
K-Means Algorithm
-
Input
-
K - number of clusters
-
Training Set

-
-
Overview Steps
-
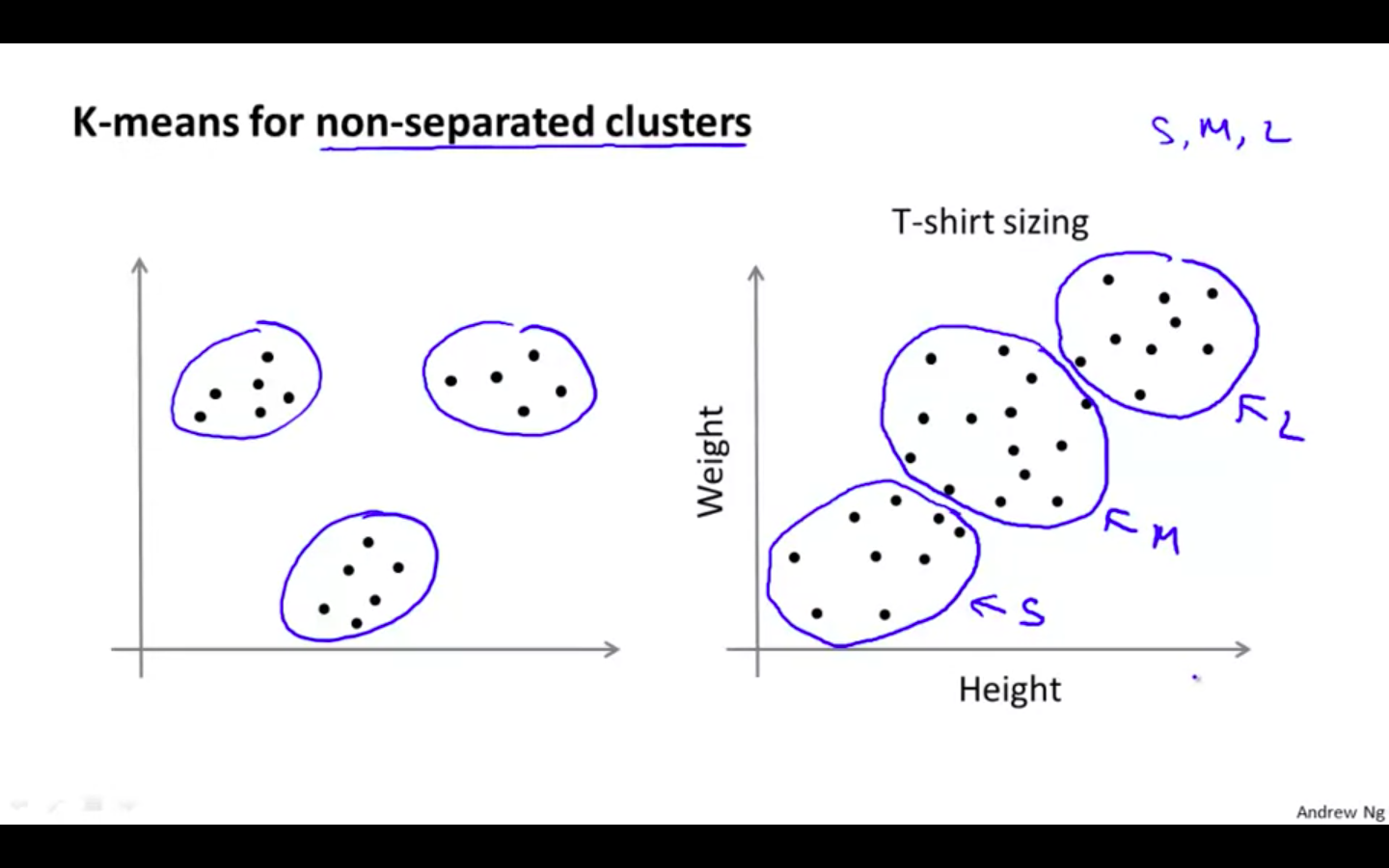
For Non-Separated Data
-
Optimisation Objective
-
Optimisation Objective
- Minimise the distance between the actual point and the centroid of the cluster associated
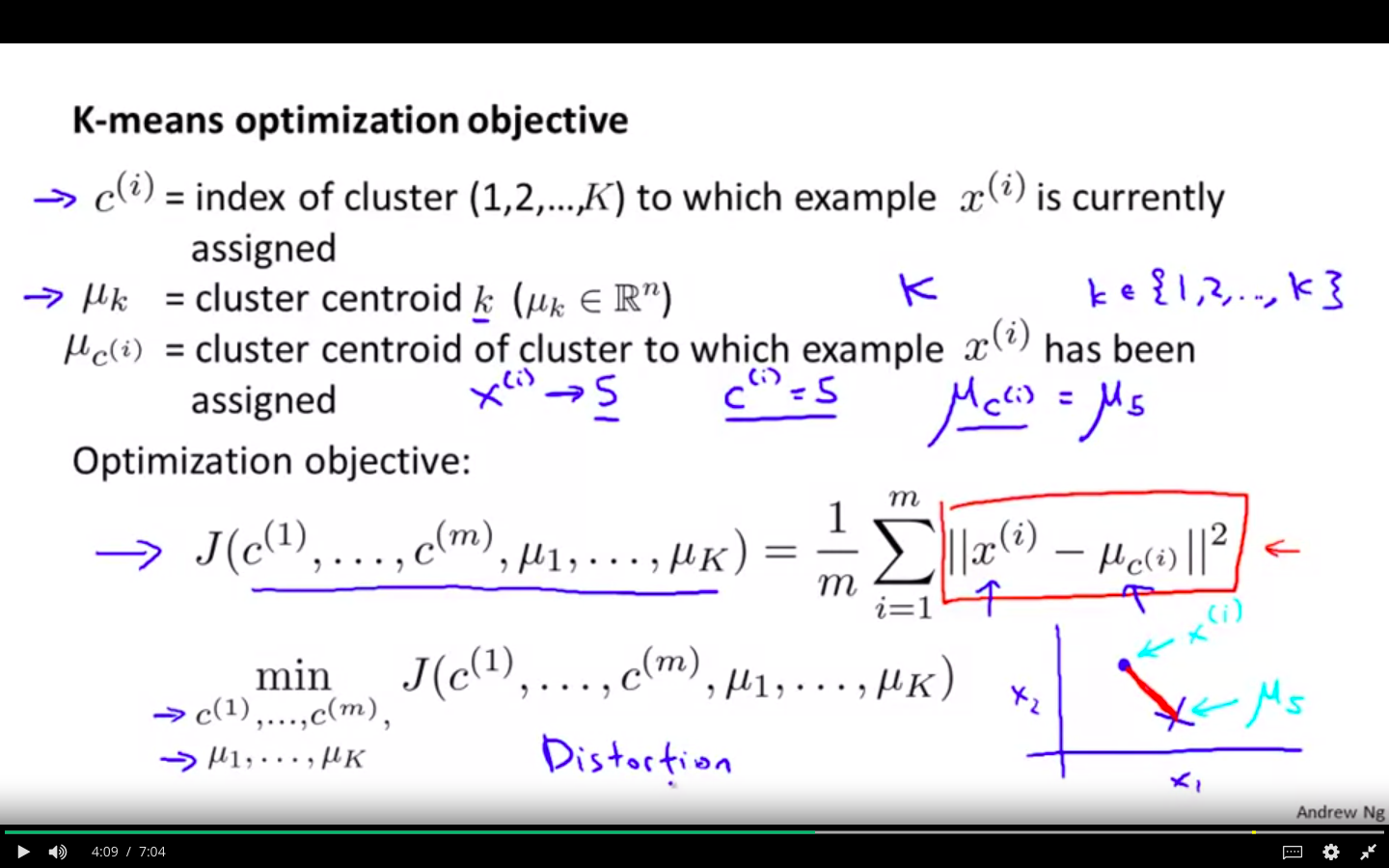
-
Algorithm
-
First part of the algorithm consist of minimising cost function with respect to c^i holding u_k fixed
-
Second part of the algorithm consist of minimising cost function with respect to u_k
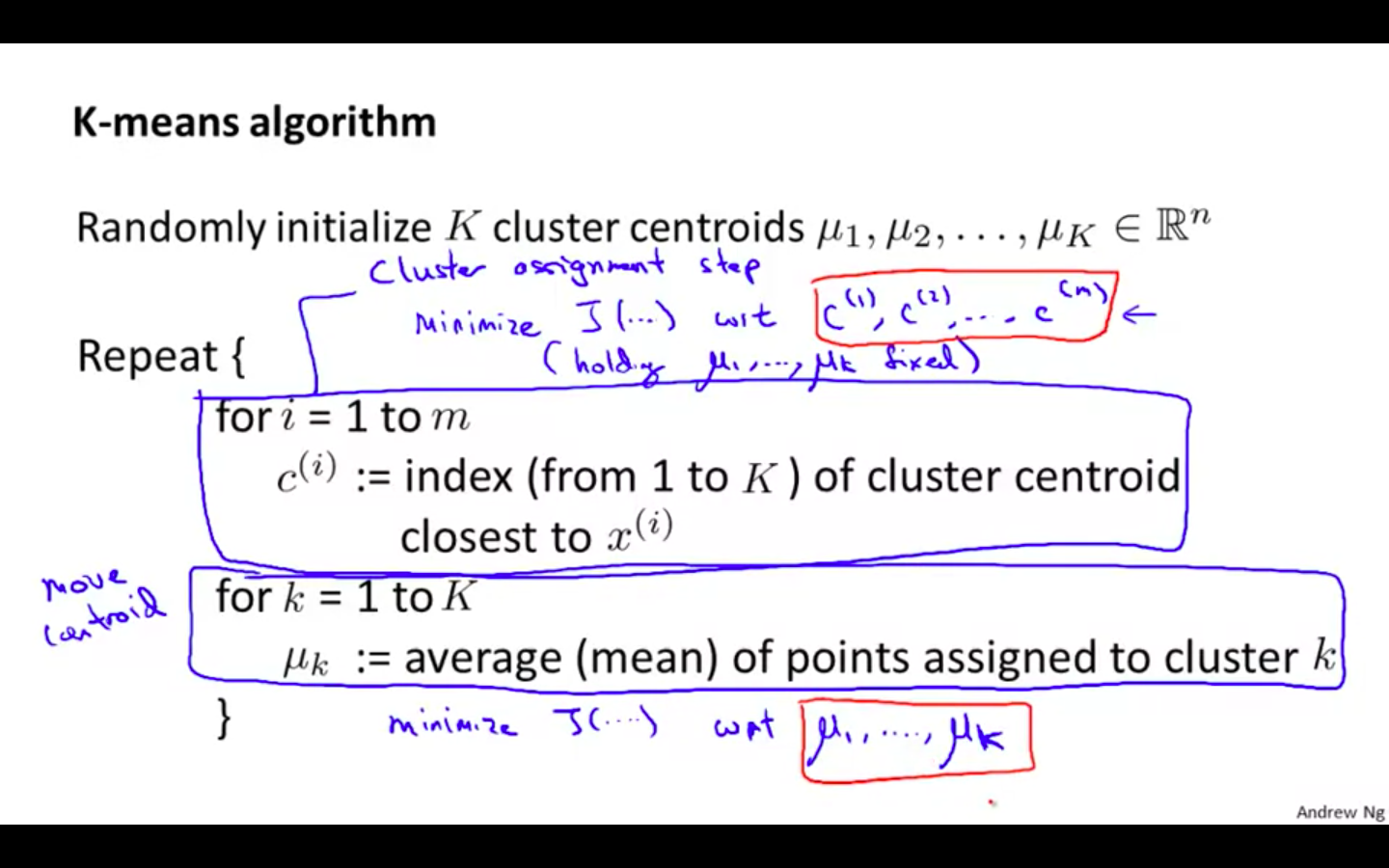
-
Random Initialisation
-
Random Initialisation
- Should have K < m
- Randomly pick K training examples
- Set u_1….u_k to these K examples
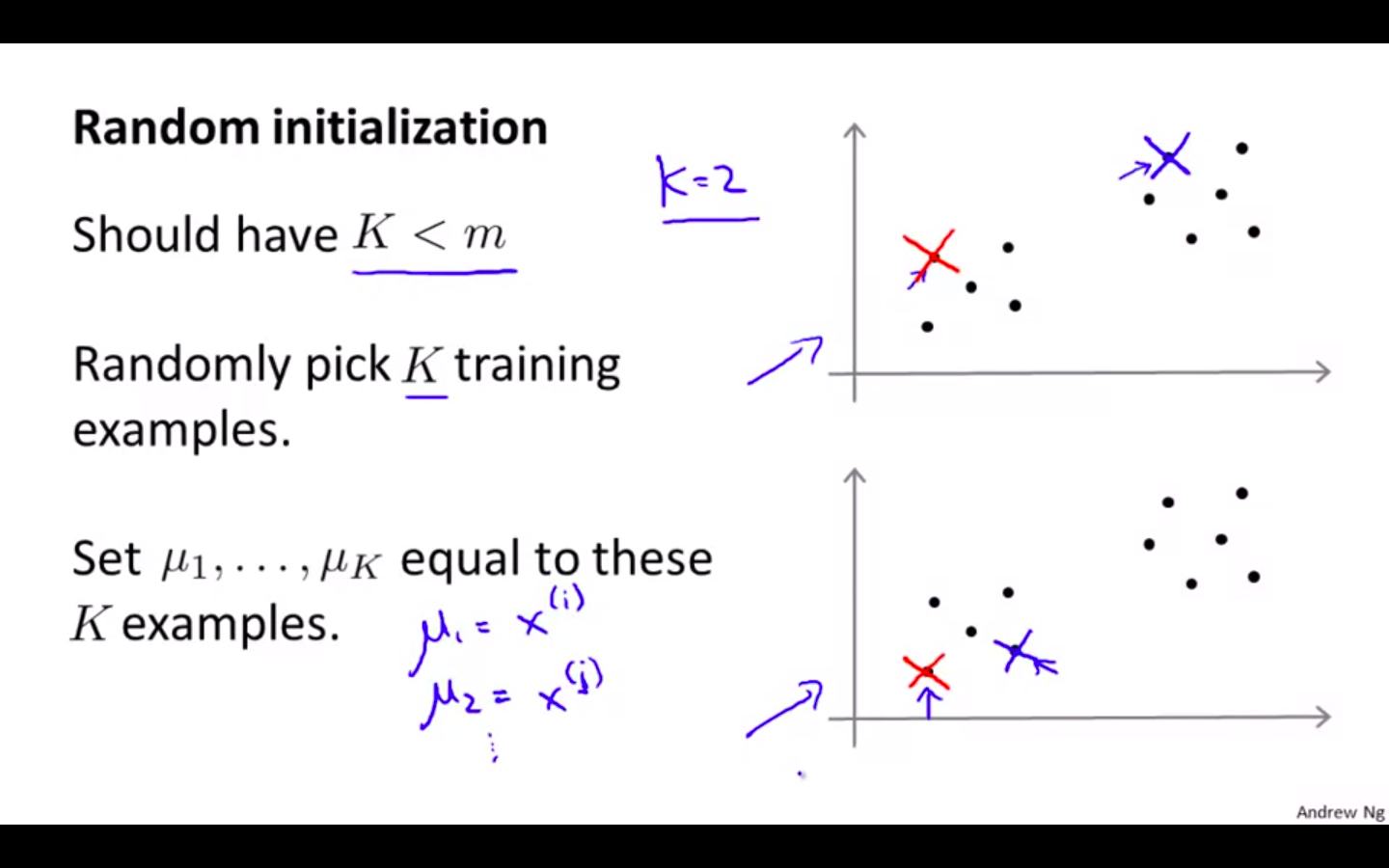
-
Local Optima
- K-Means can get stuck at local optima
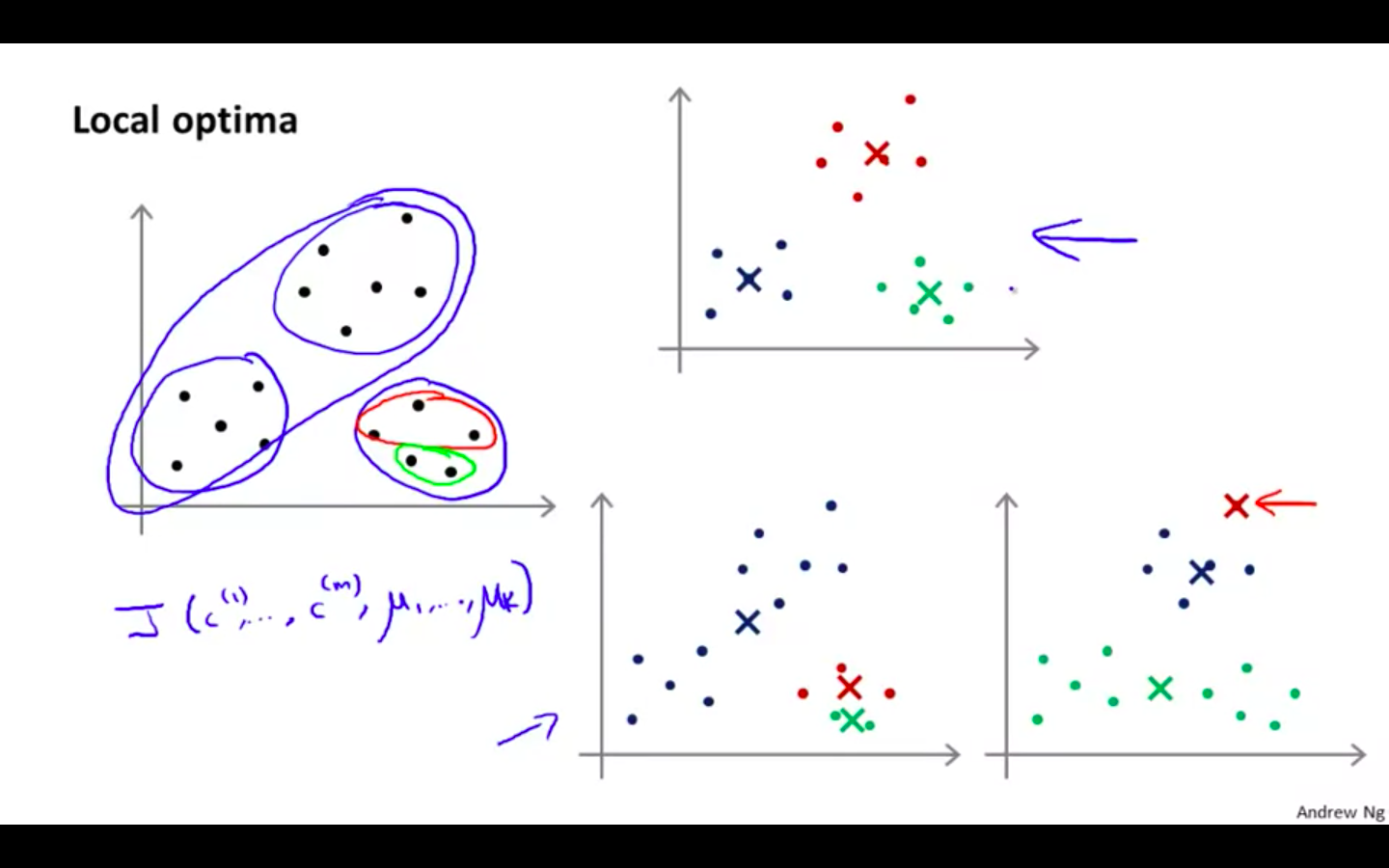
-
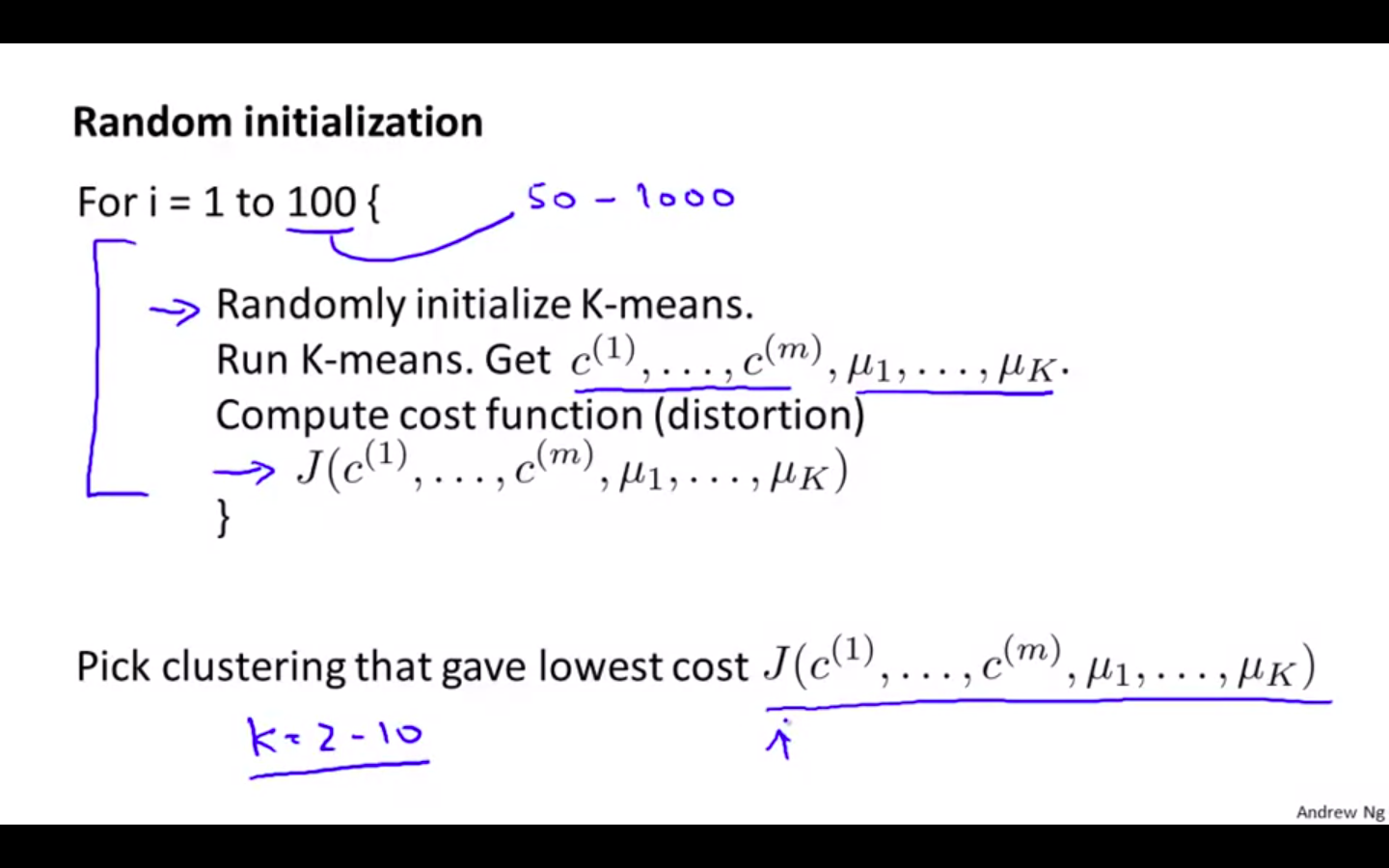
Random Initialisation Extended
-
Run K-Means for n number of times
- n = 50 to 1000
-
Pick the iteration which gives the minimum cost function
-
Choosing the Number of Clusters
-
What is the right value of K ?
-
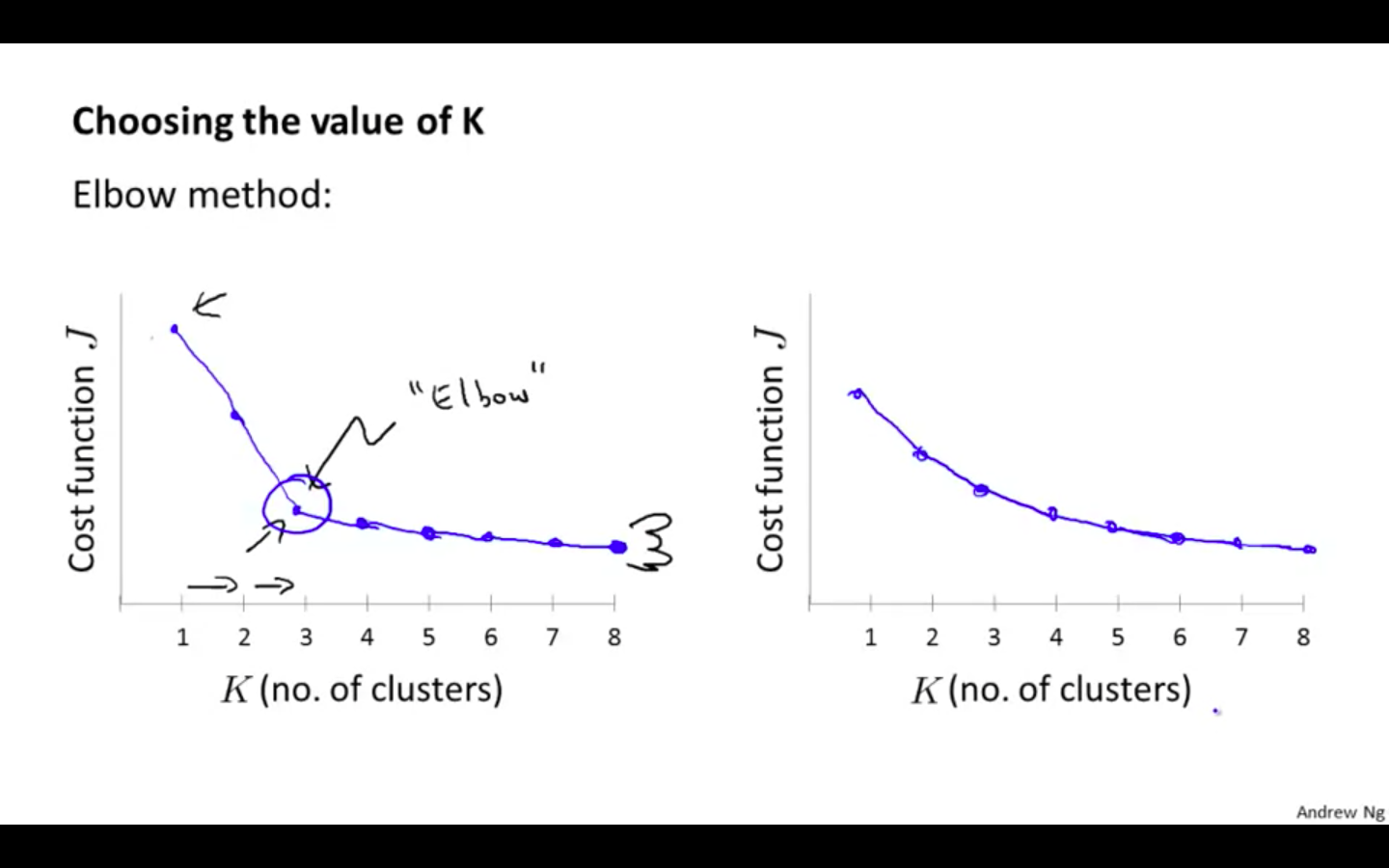
Elbow Method
-
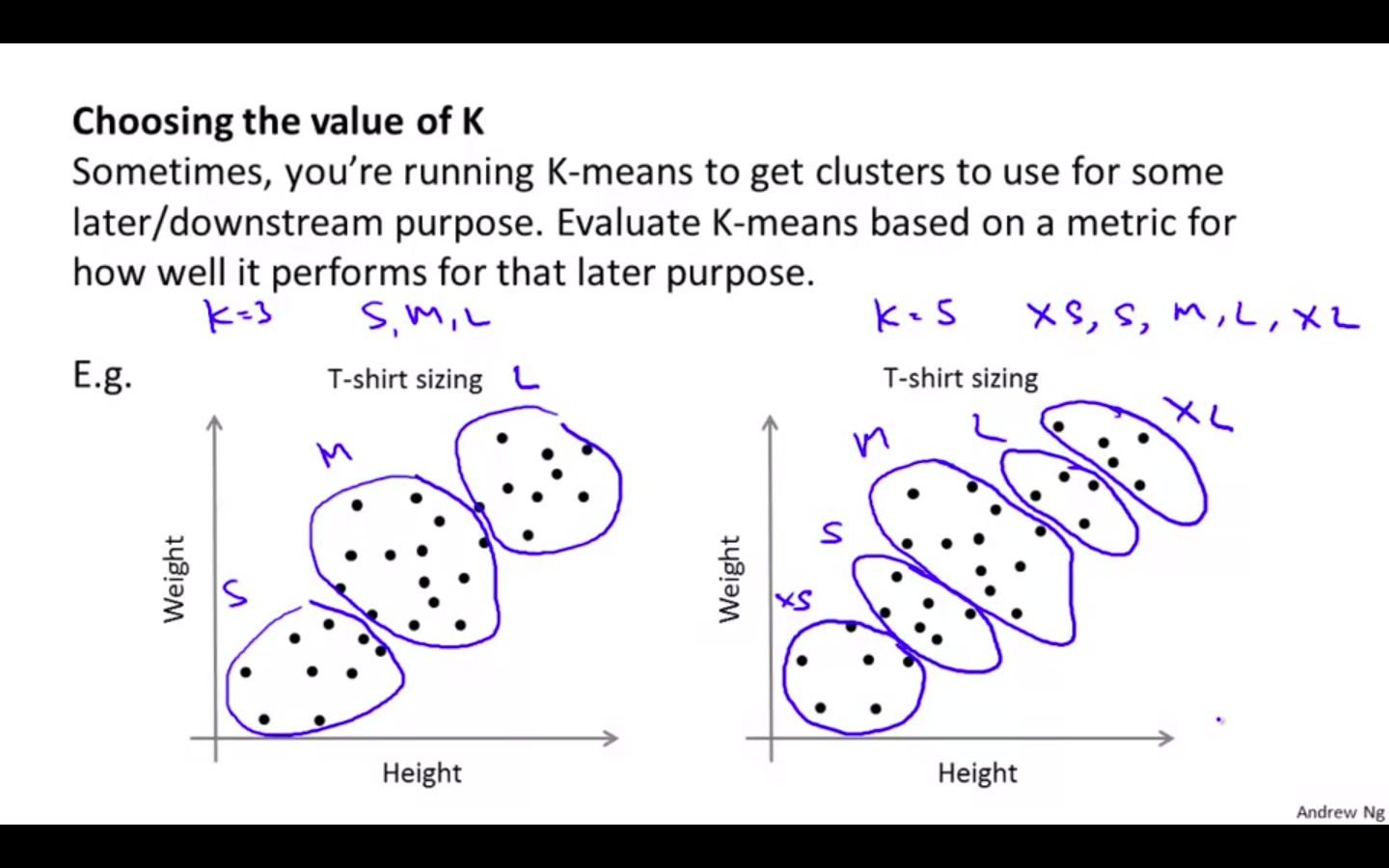
Other Method
- Choosing the value of K based on the application
Motivation
Motivation 1: Data Compression
-
Data Compression
- Compressing the size of the data
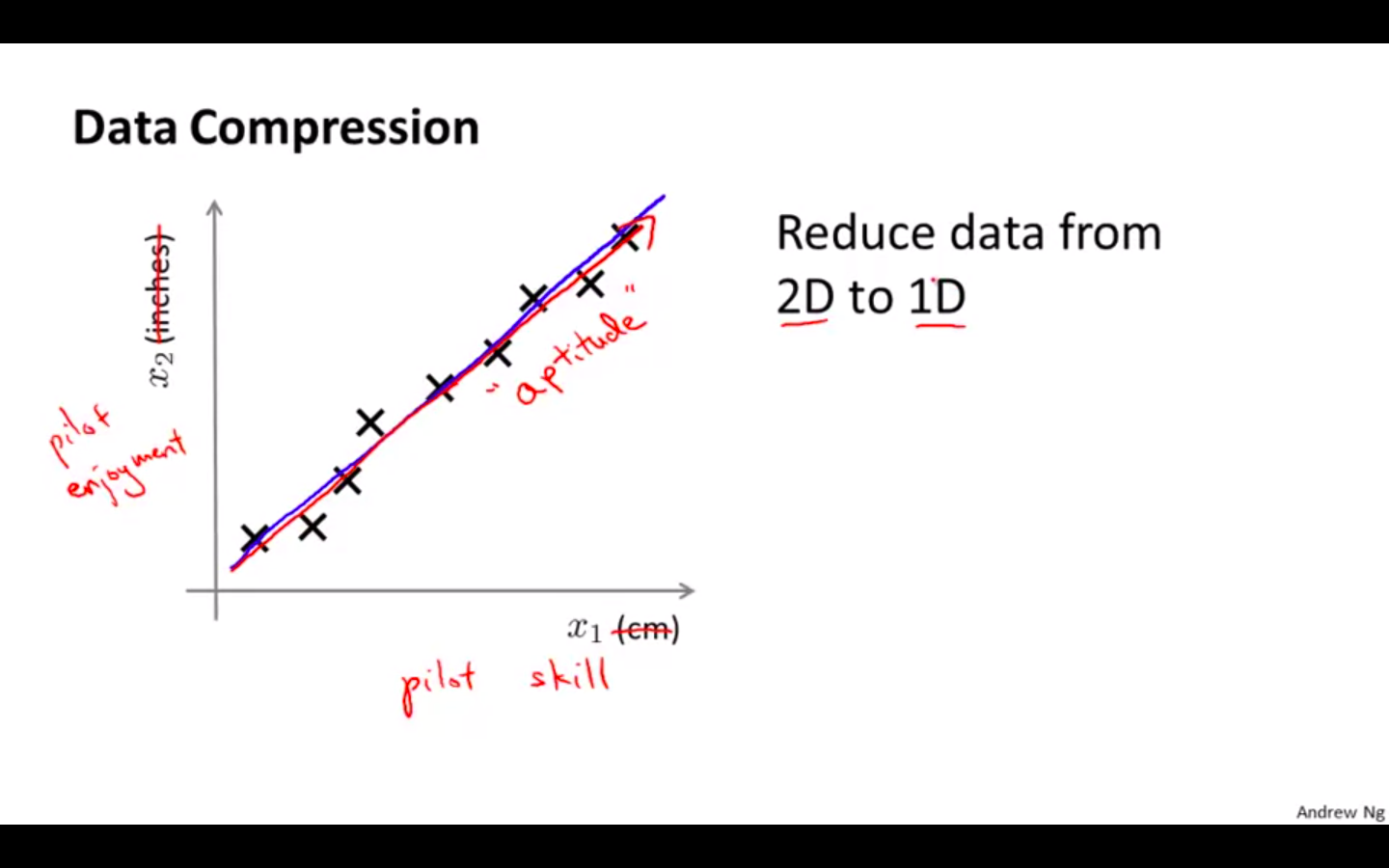
-
2D to 1D
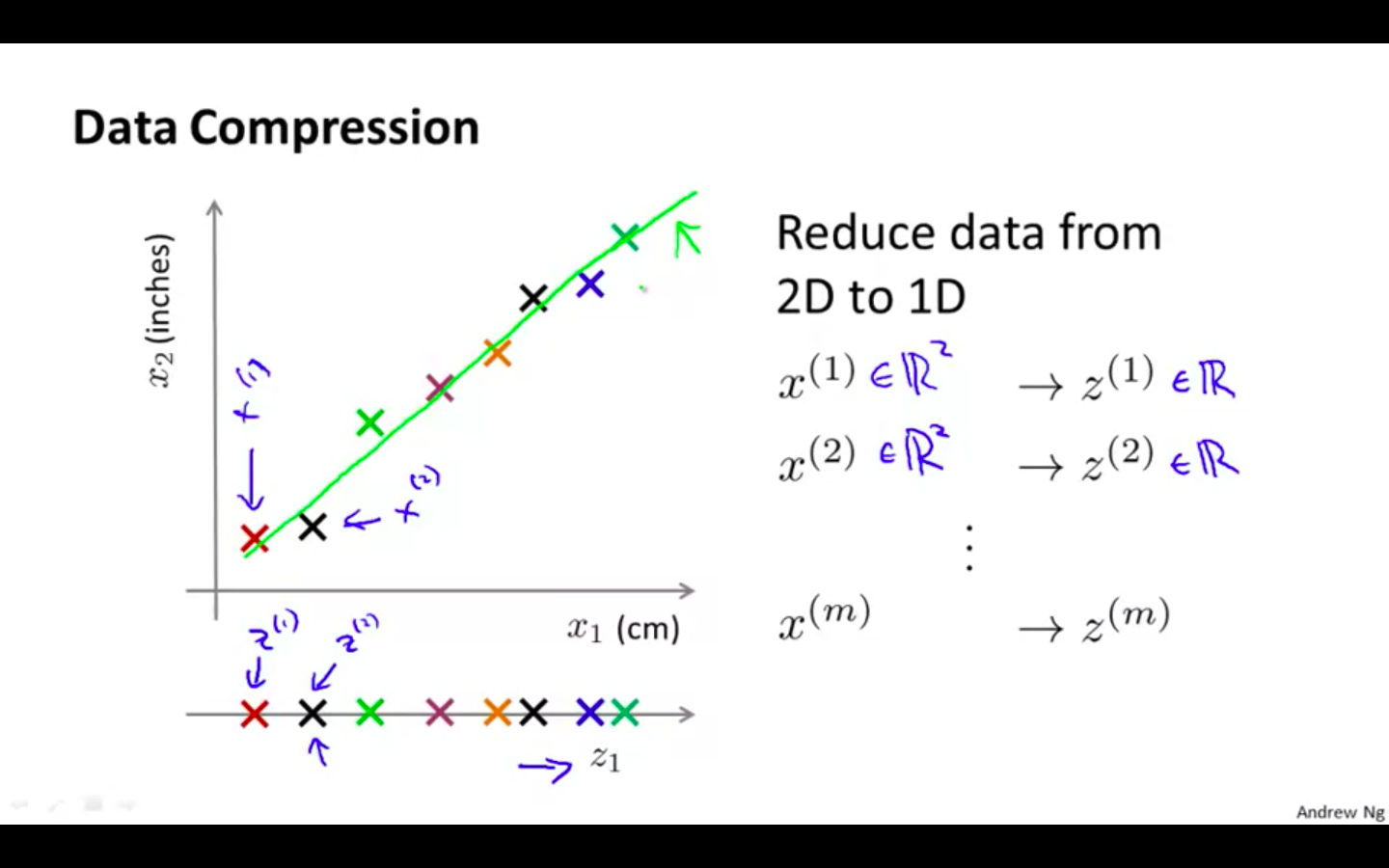
-
3D to 2D
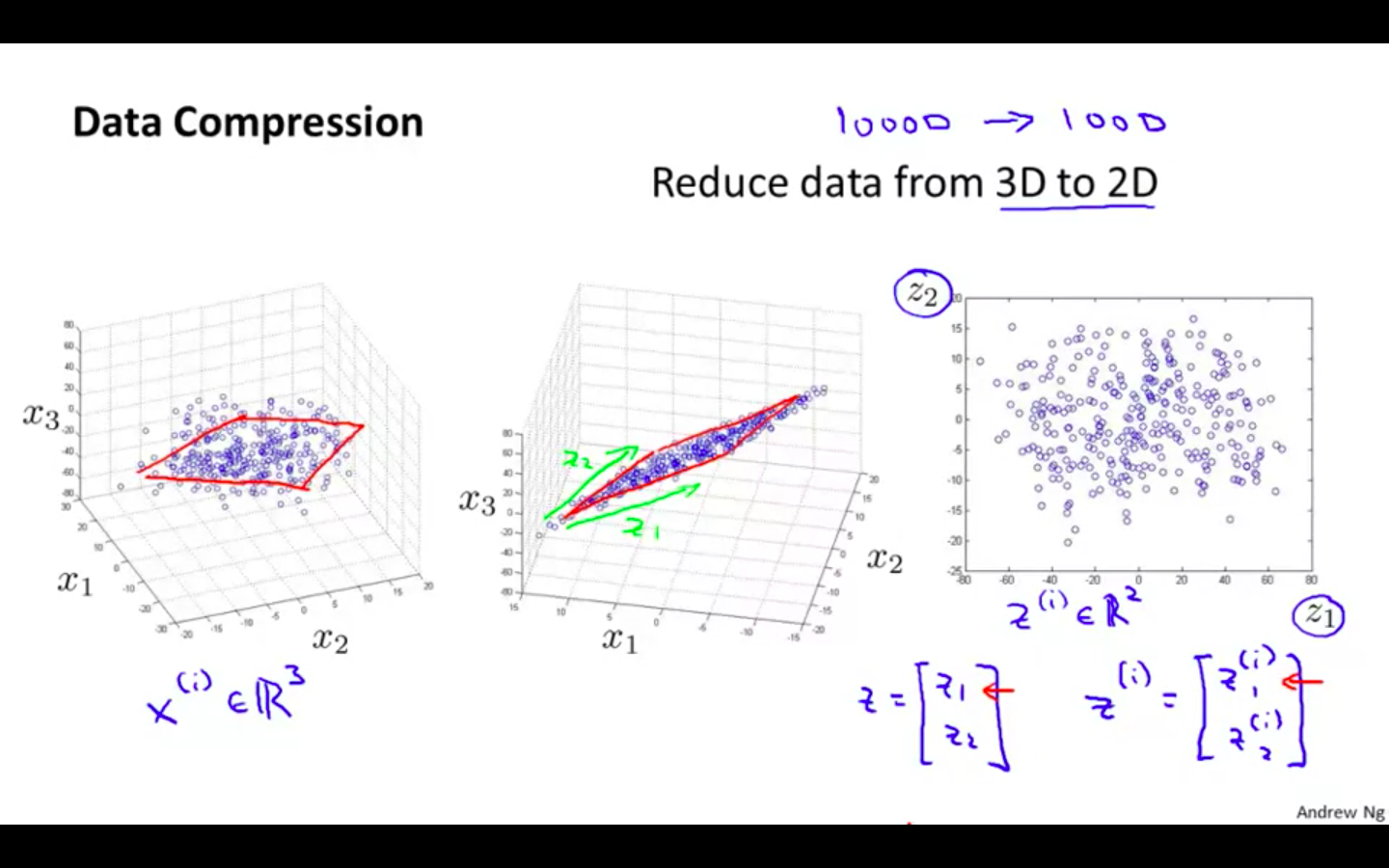
Motivation 2: Visualisation
-
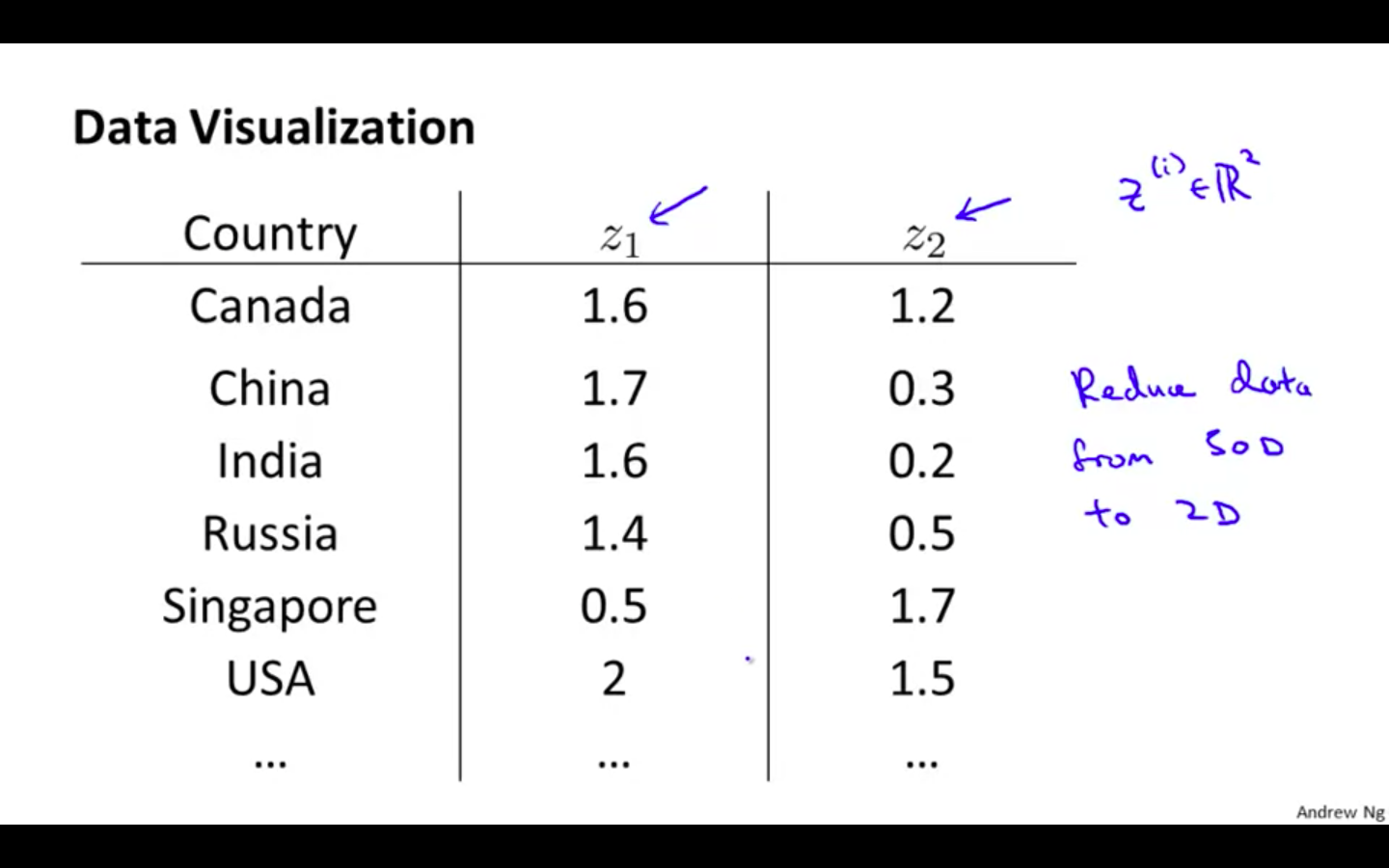
Data Visualisation
- Dataset of countries with many features
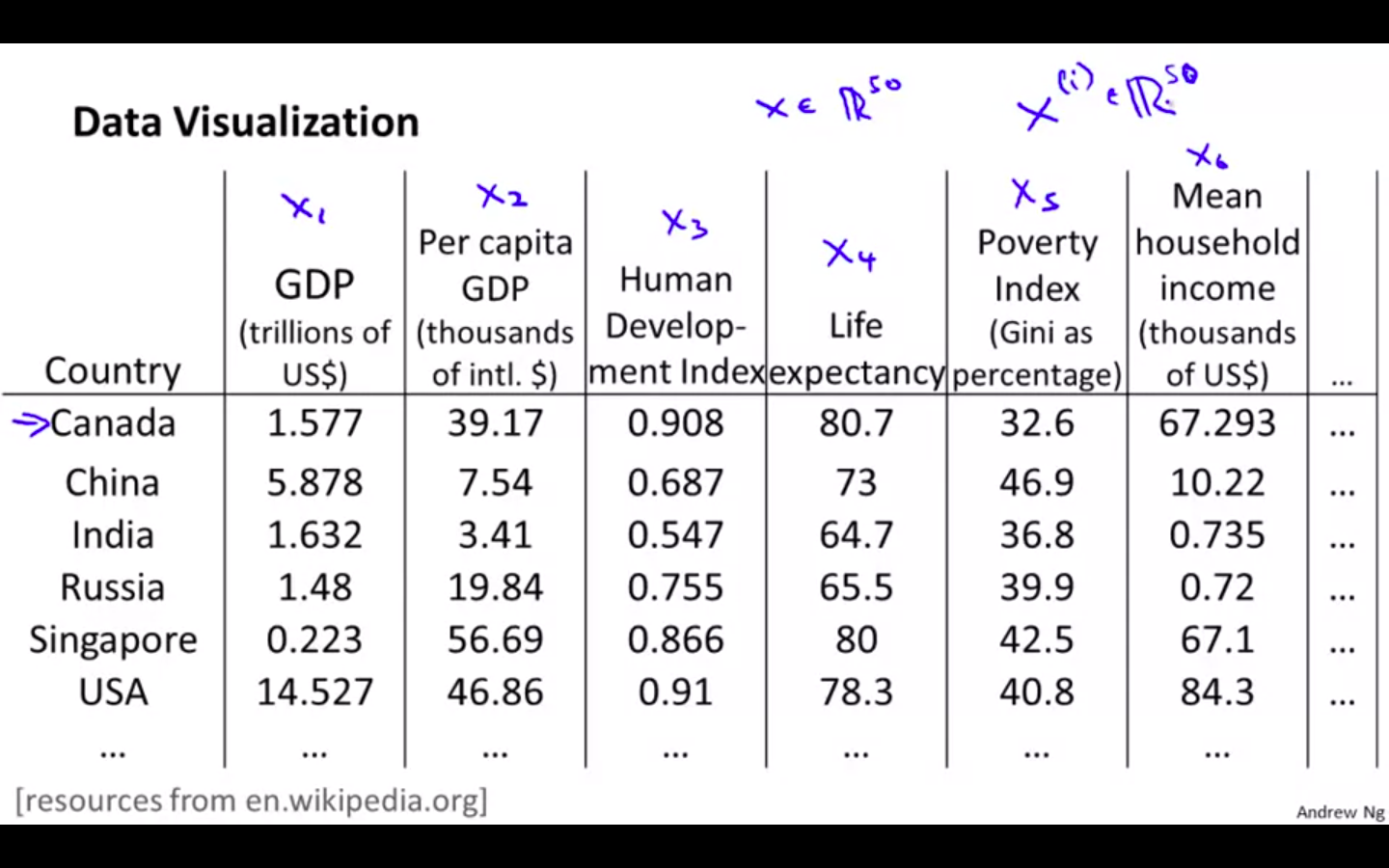
- Converting 50 D to 2 D
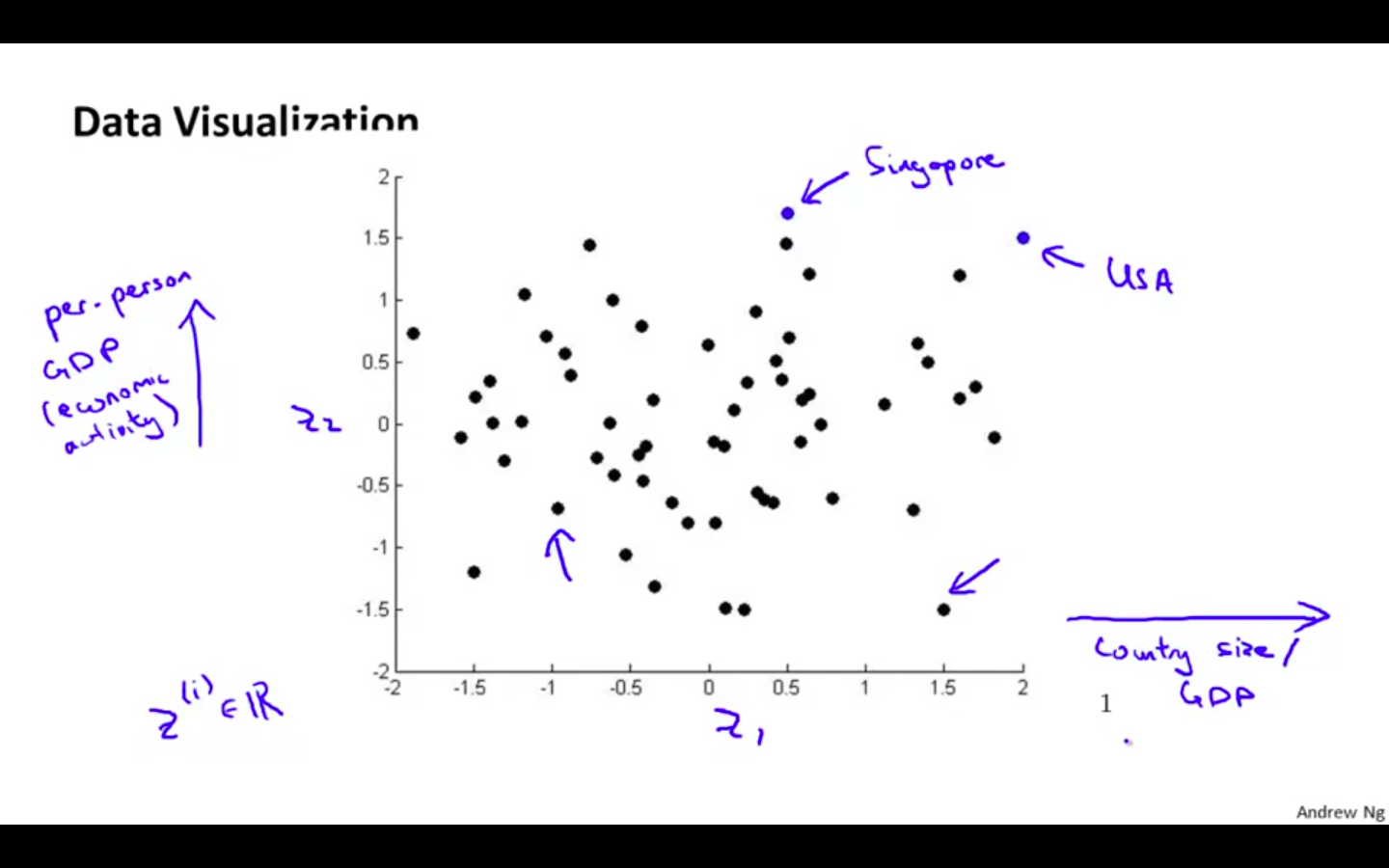
- Plotting the dataset
Principal Component Analysis
Principal Component Analysis Problem Formulation
-
PCA
- Dimension Reductionality Algorithm
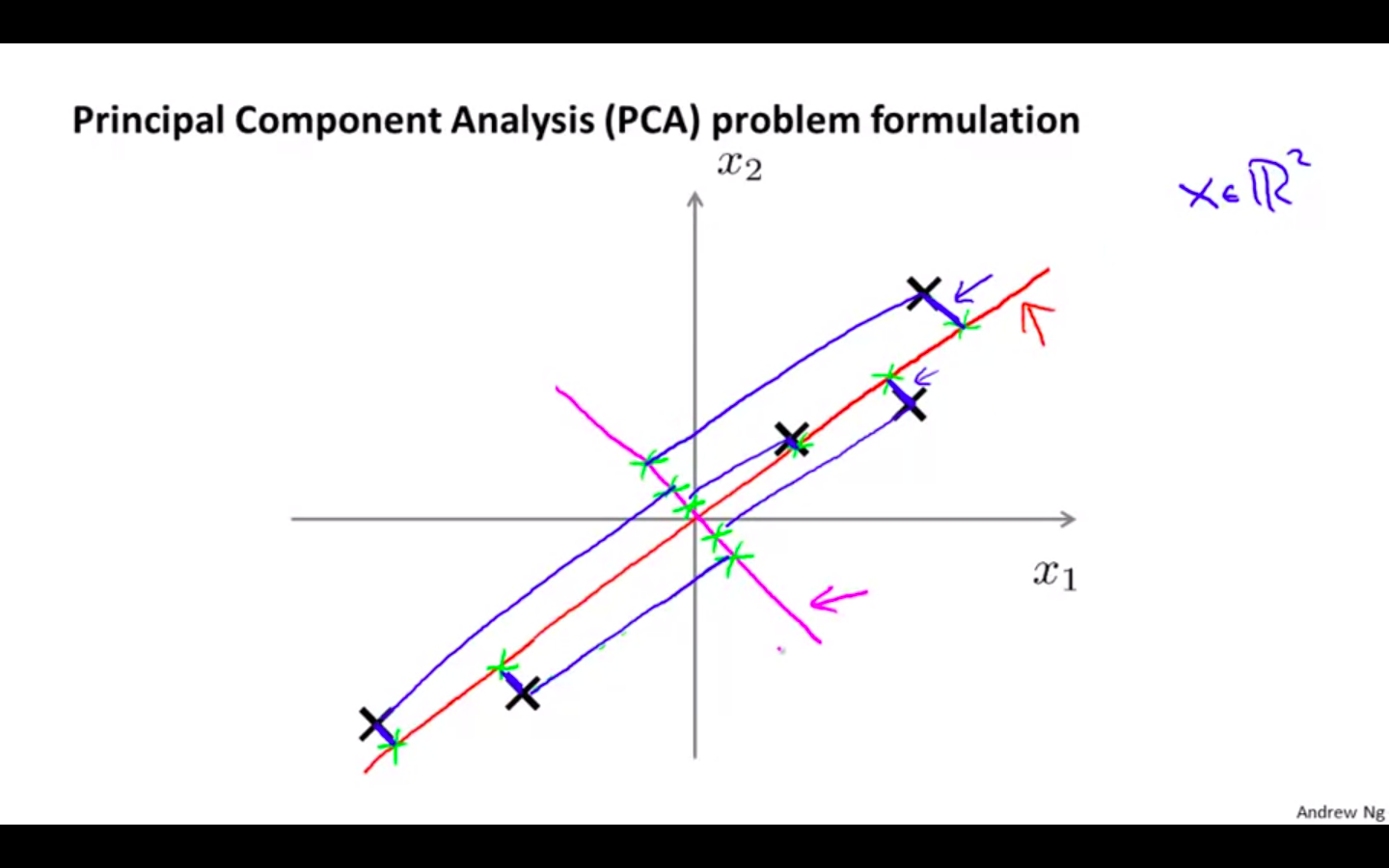
- Problem Formulation
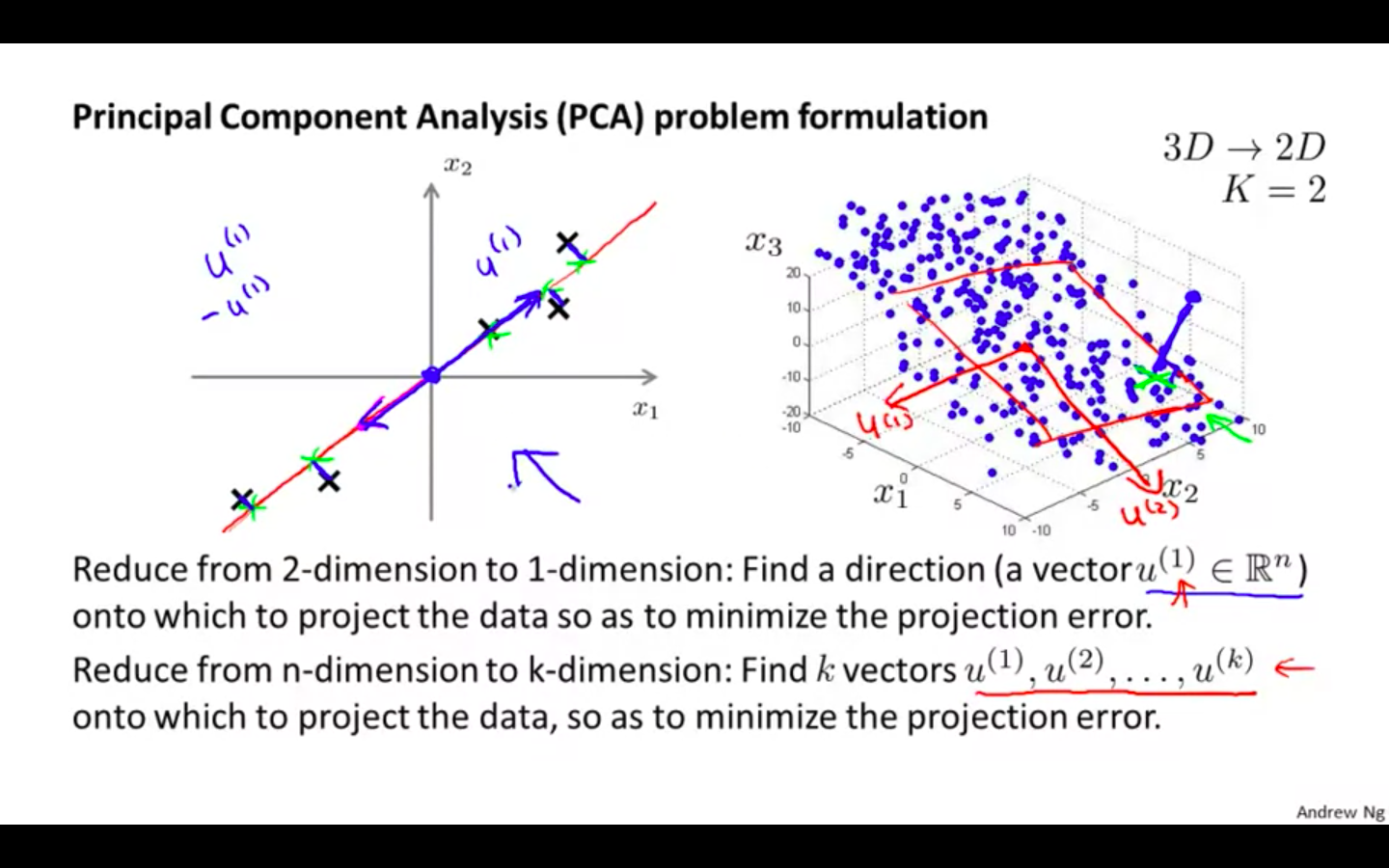
-
PCA is not Linear Regression
-
In linear regression, the error is draw 90 degree from the line to the data point
-
In PCA, the projection error is drawn at a angle from the line to the data point
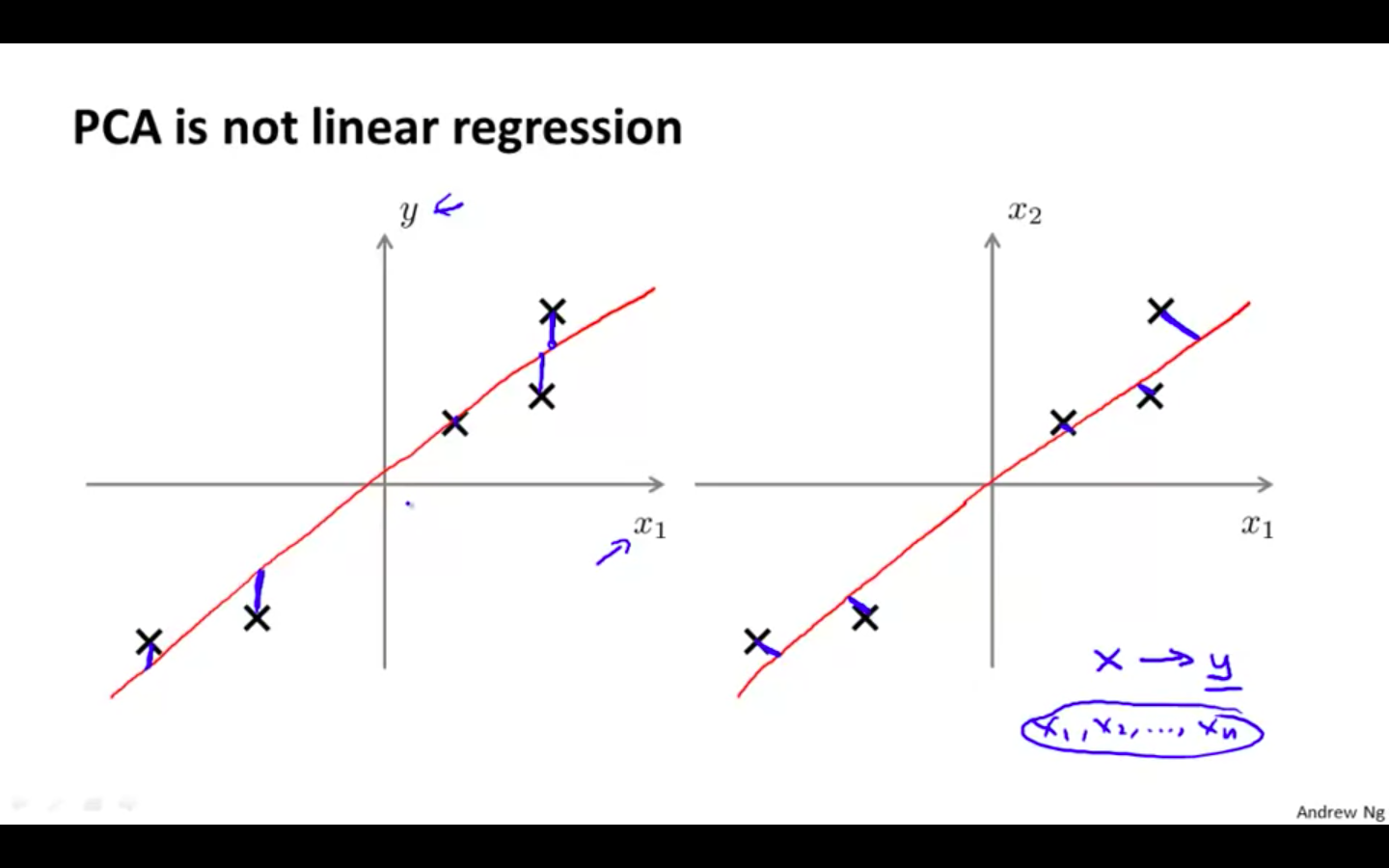
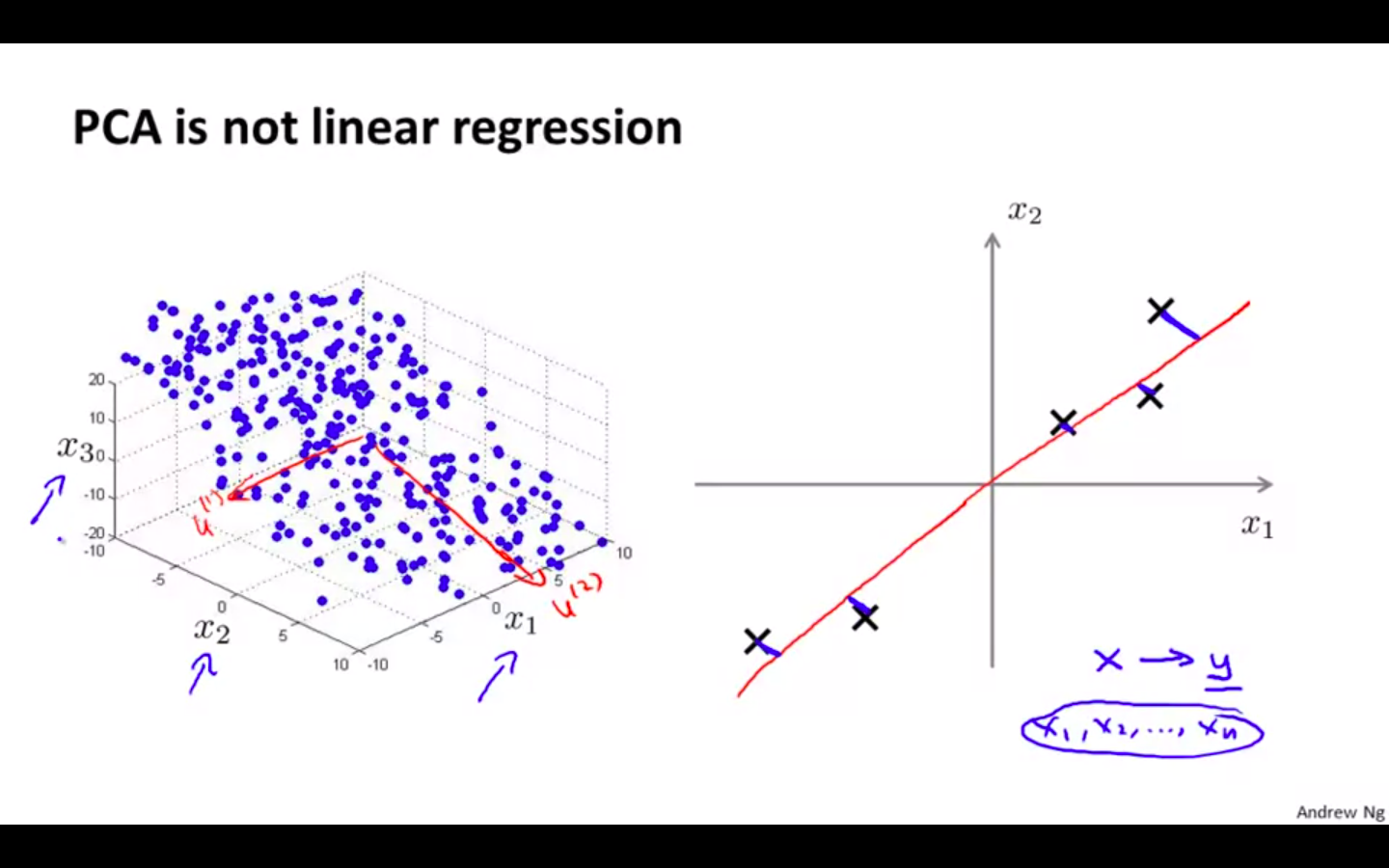
-
Principal Component Analysis Algorithm
-
Data Preprocessing
- Mean Normalisation
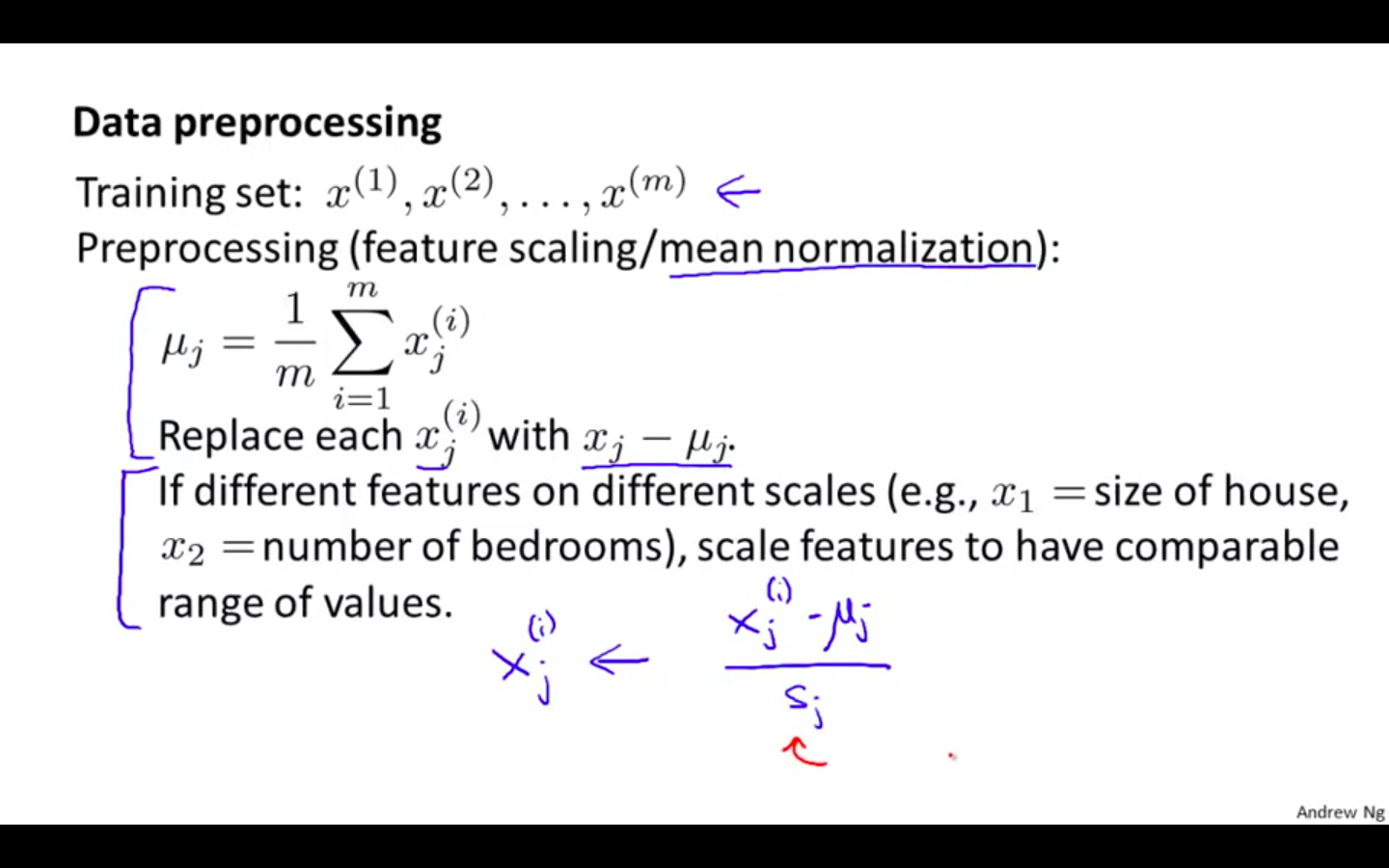
-
PCA Algorithm
- Reducing dimension of data
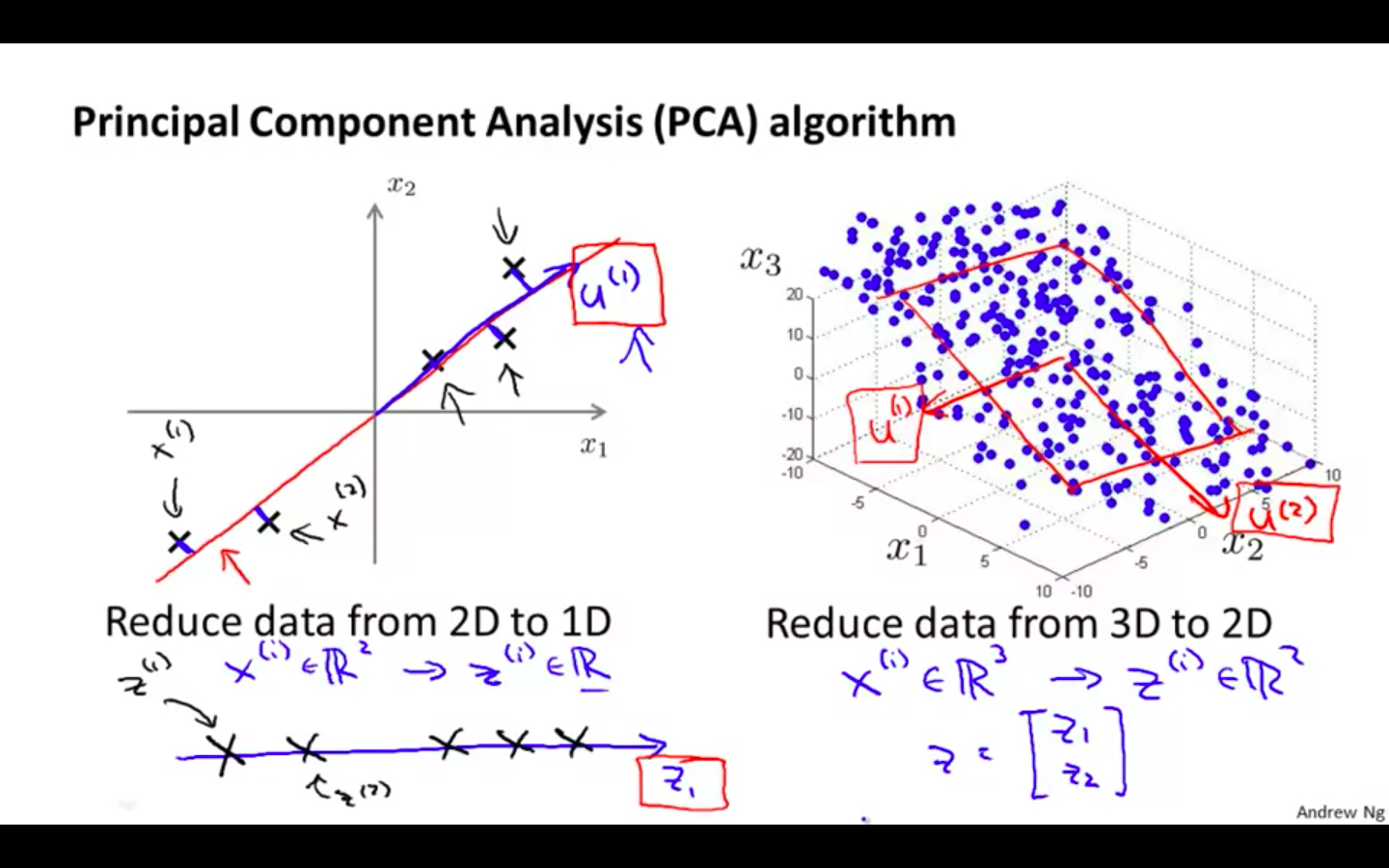
-
Compute ‘Covariance Matrix’
-
Compute ‘eigenvectors’ of matrix
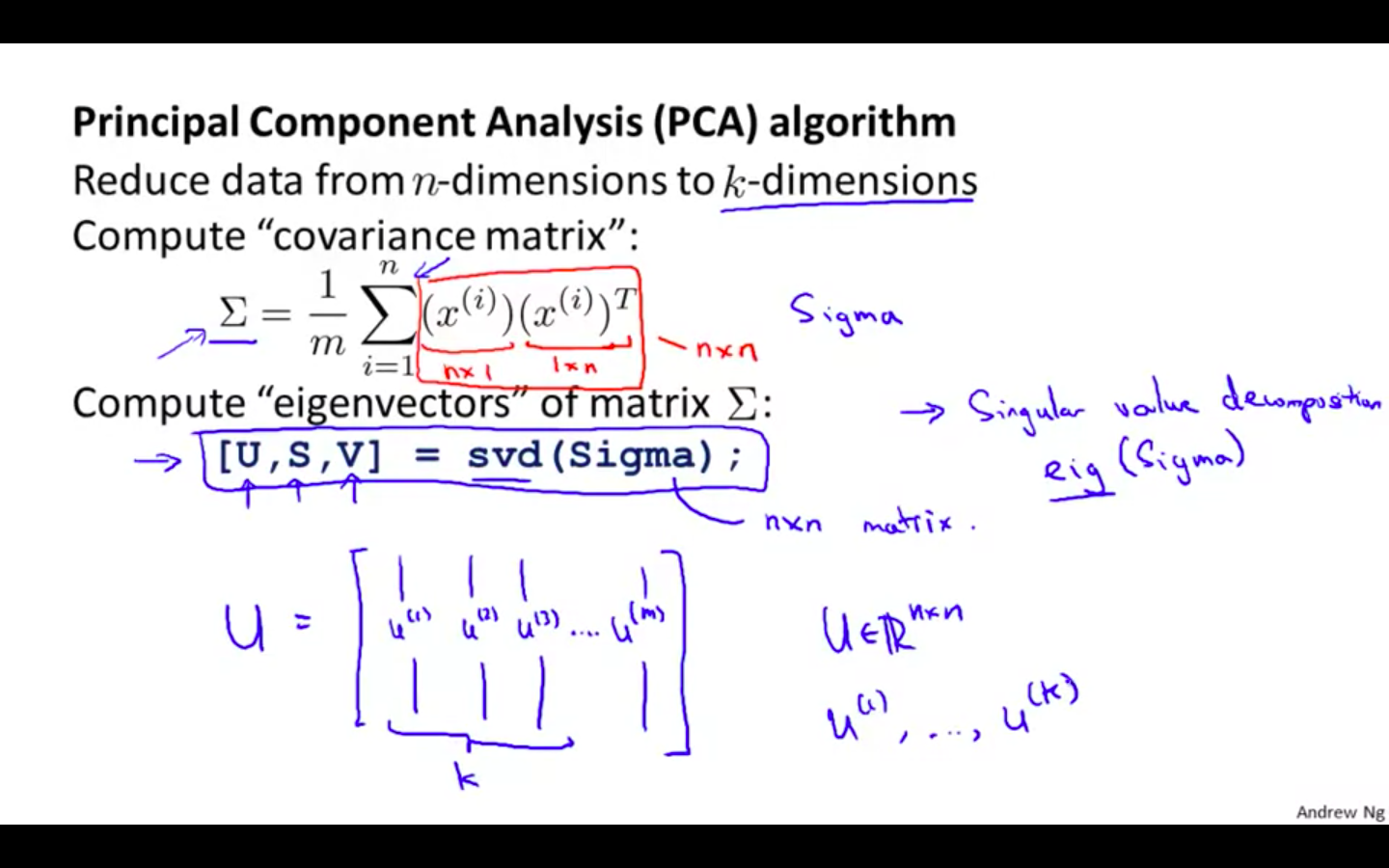
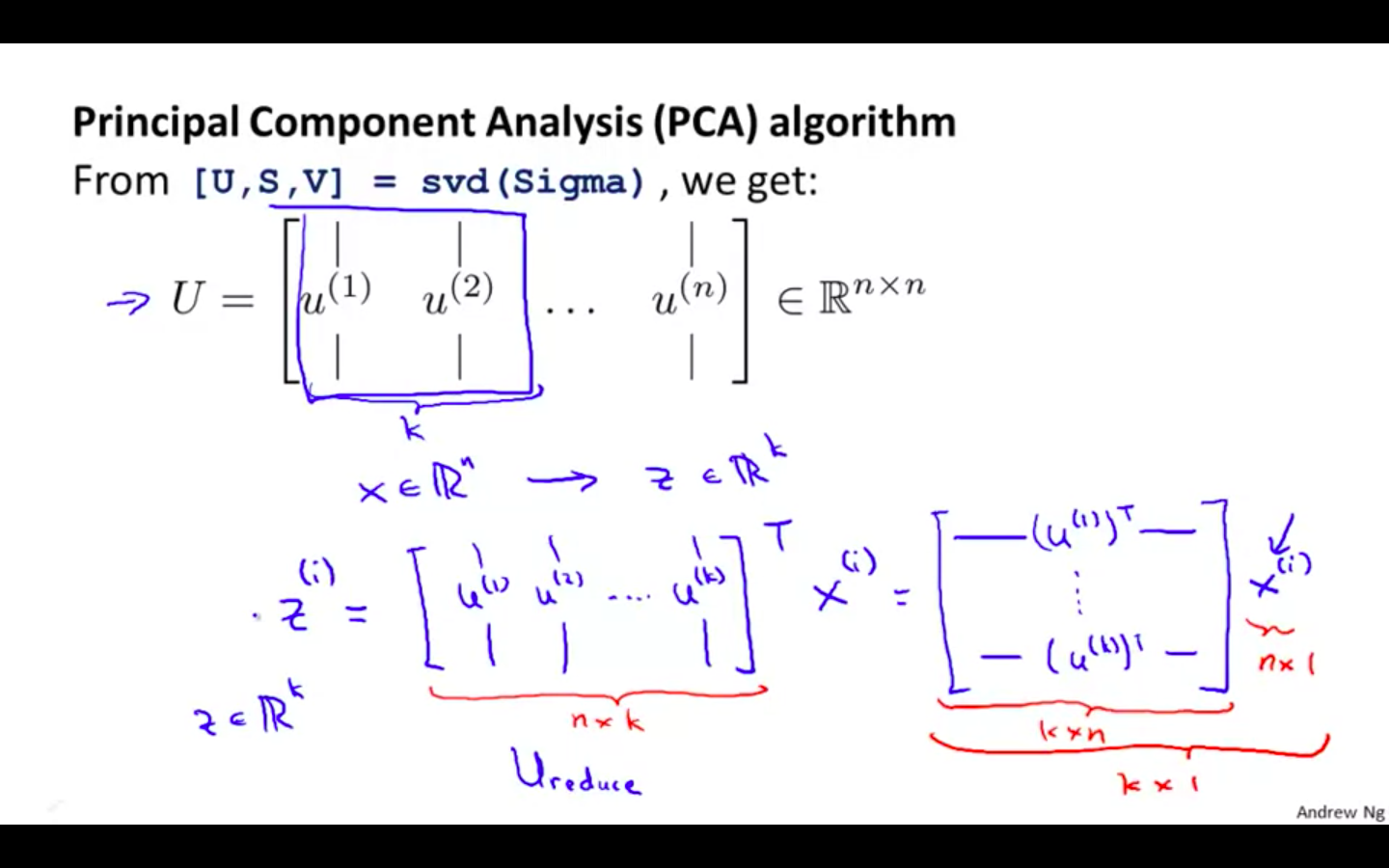
- Summary
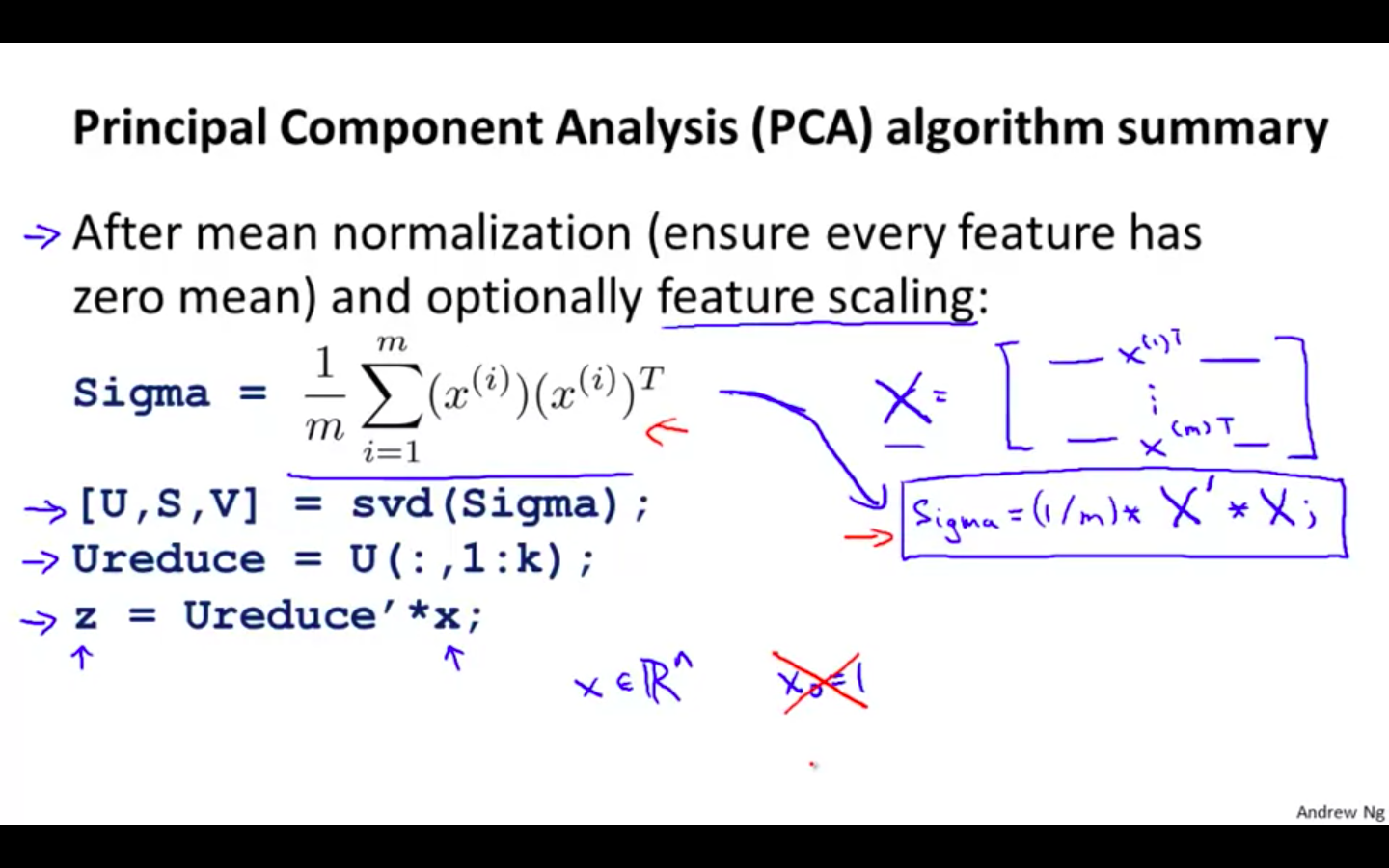
Applying PCA
Reconstruction from Compressed Representation
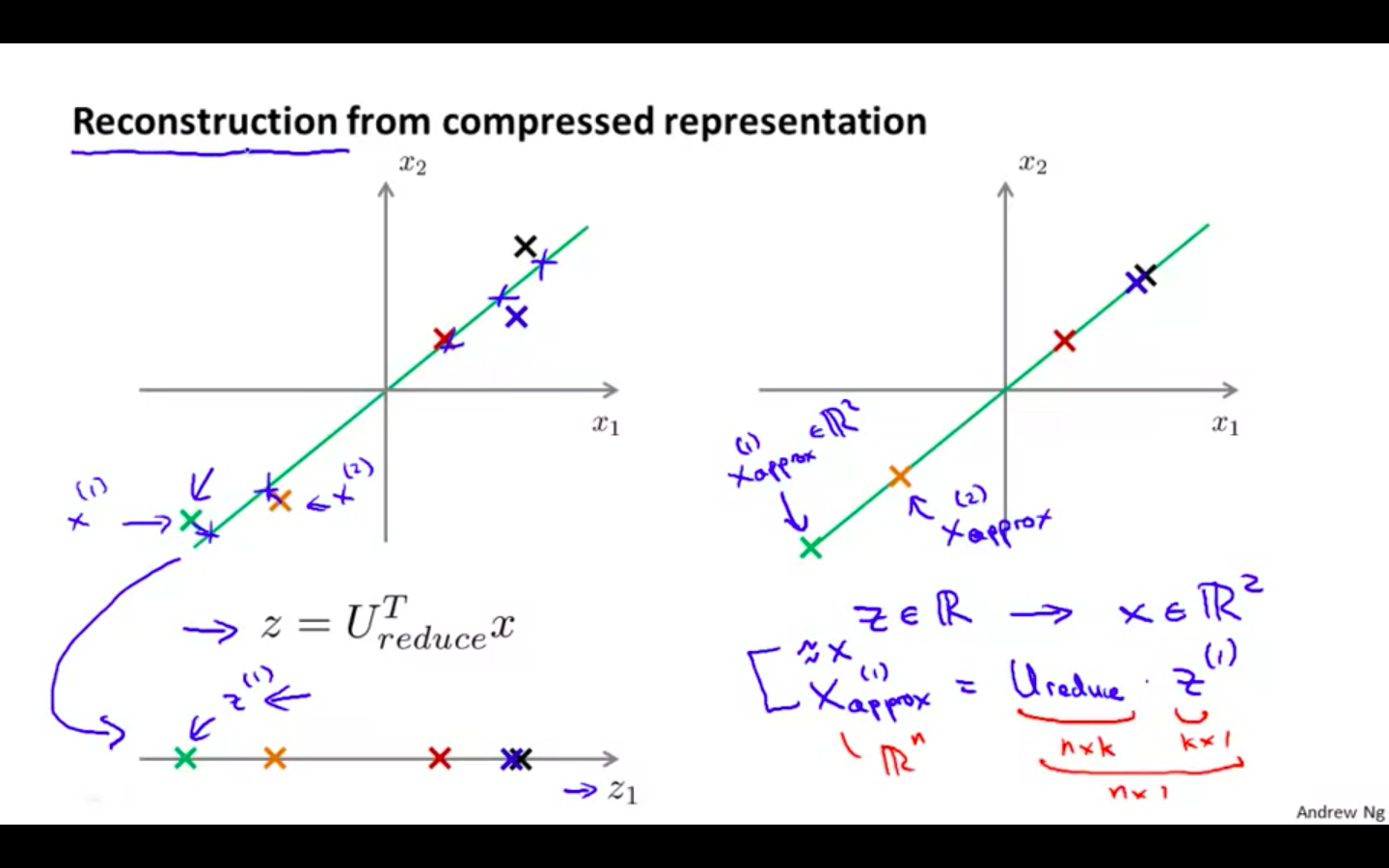
Choosing the Number of Principal Components
-
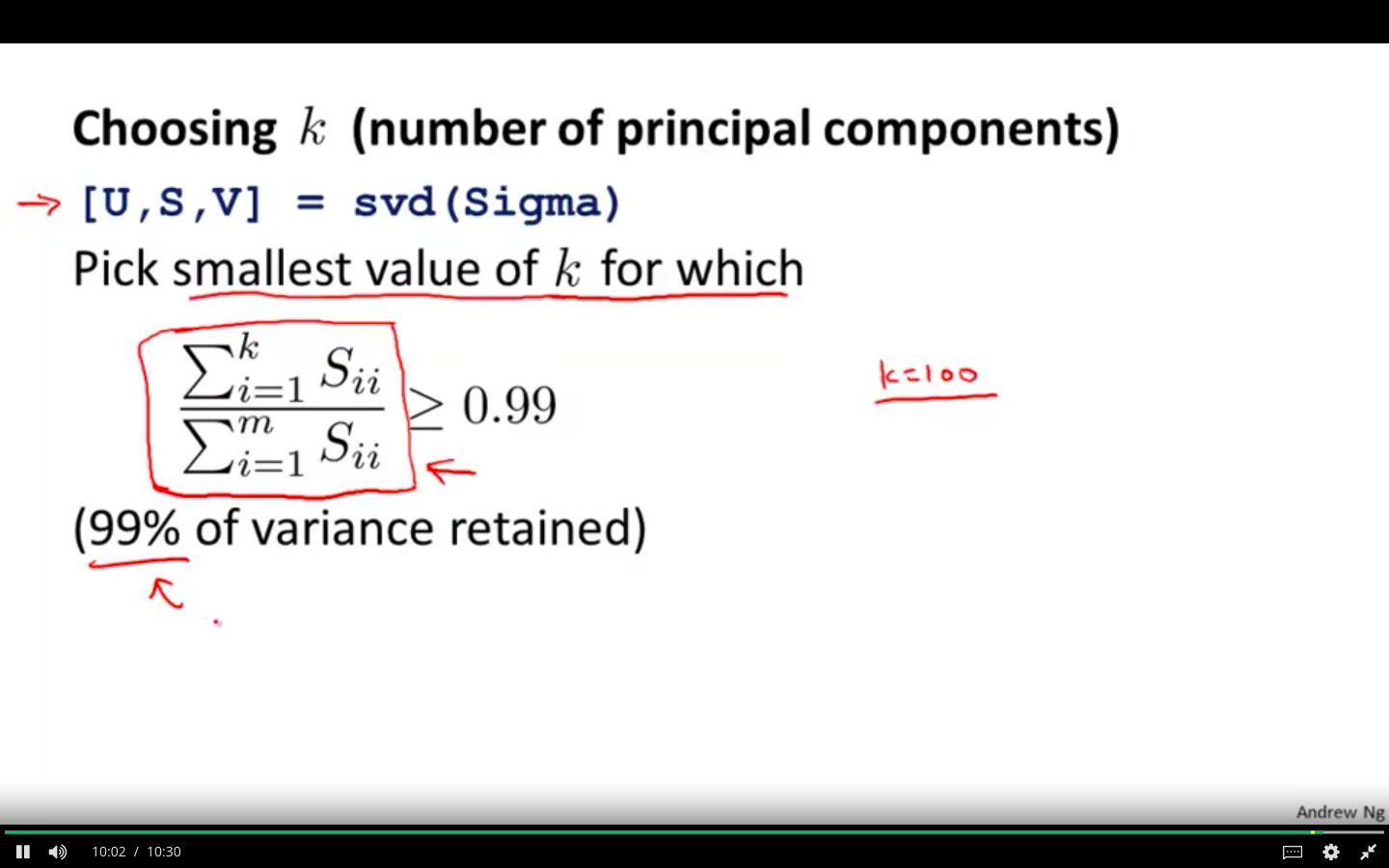
Choosing k ( number of principal components )
-
Average squared projection error / Total variation in the data ≤ 0.01
-
99 % of variance is retained
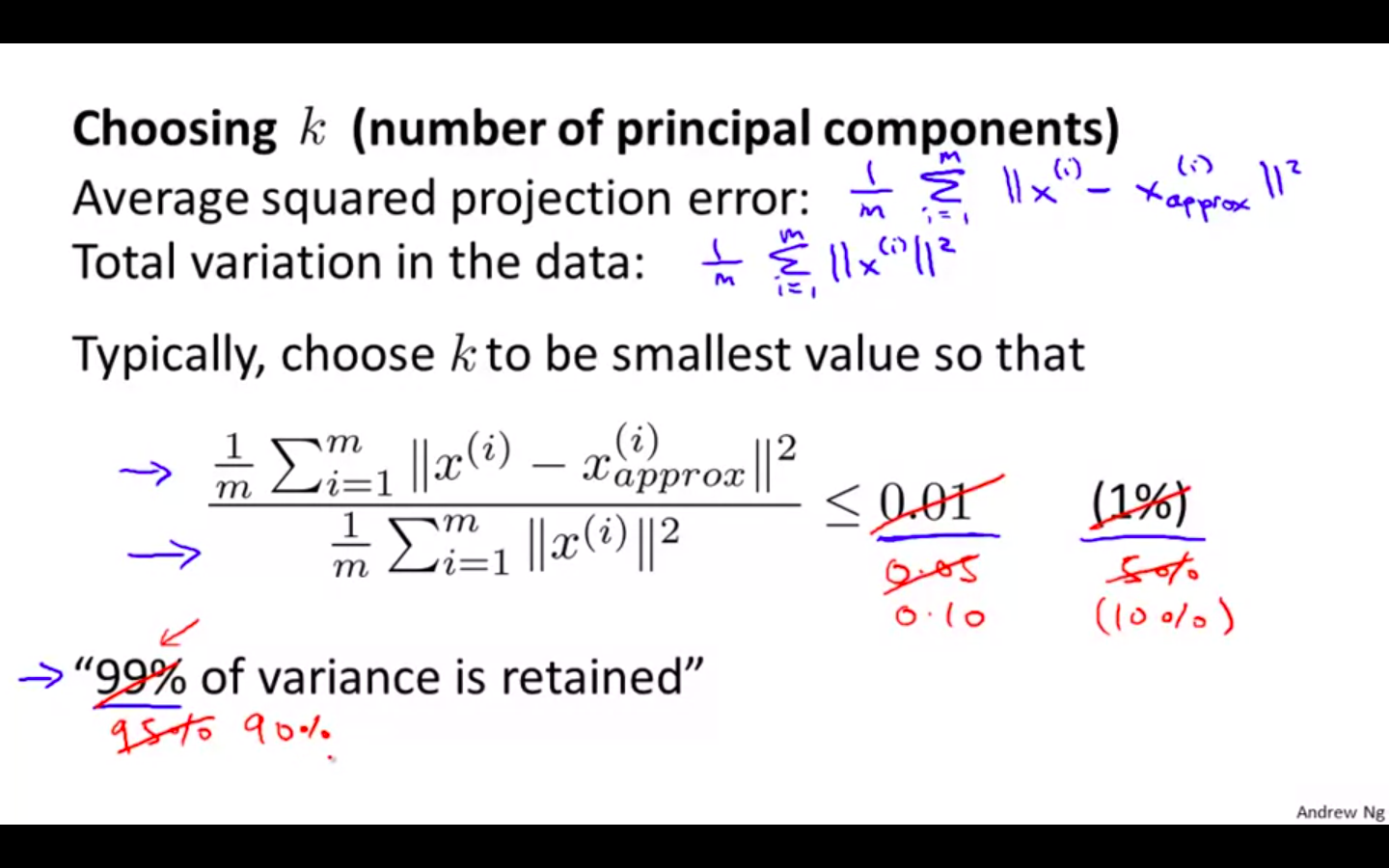
-
-
Different Algorithms
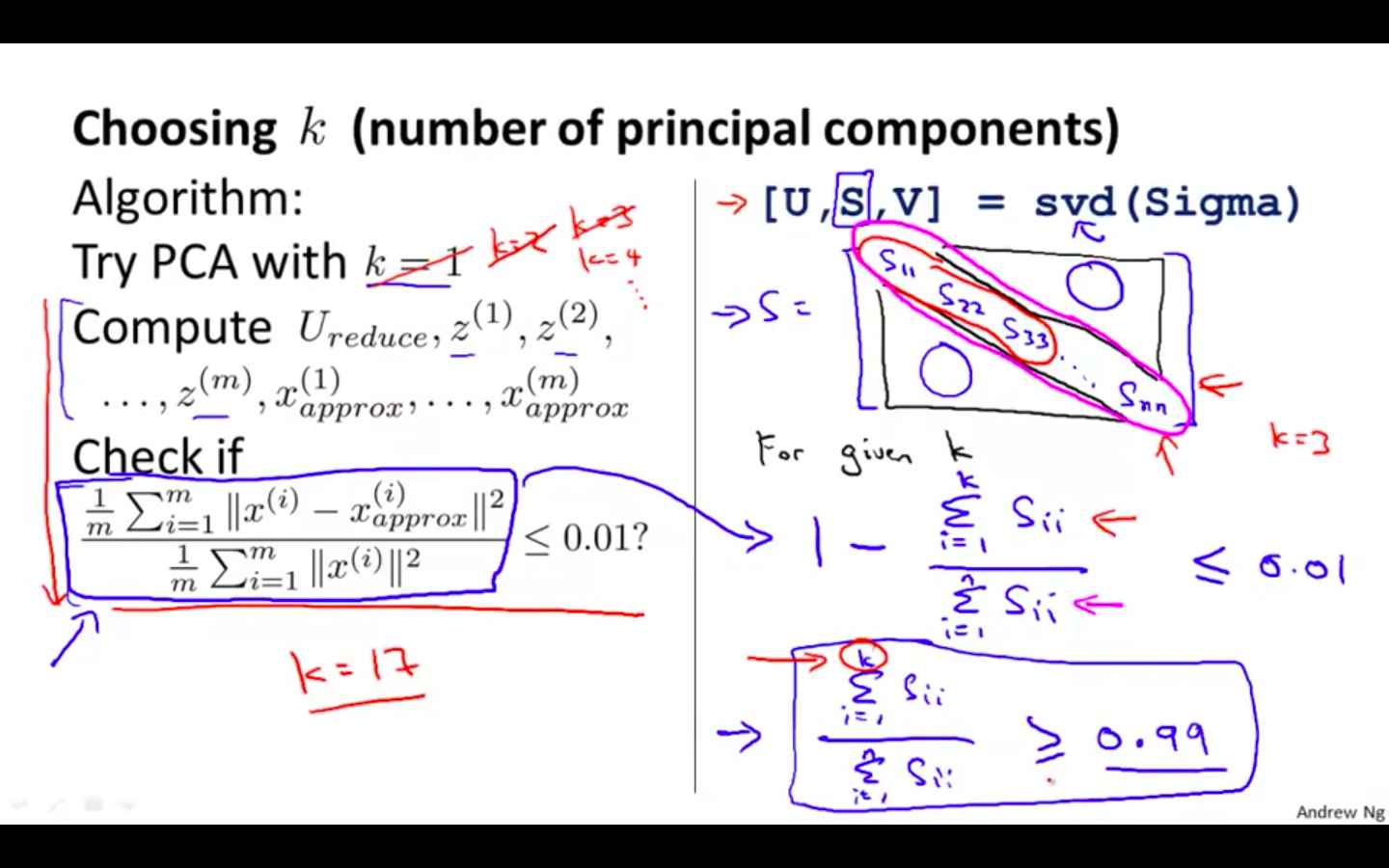
-
Recommended Method
Advice for Applying PCA
-
Supervised Learning Speedup

-
Applications
-
Compression
-
Reduce memory / disk needed to store data
-
Speed up learning algorithm
-
-
Visualisation

-
-
Bad Use
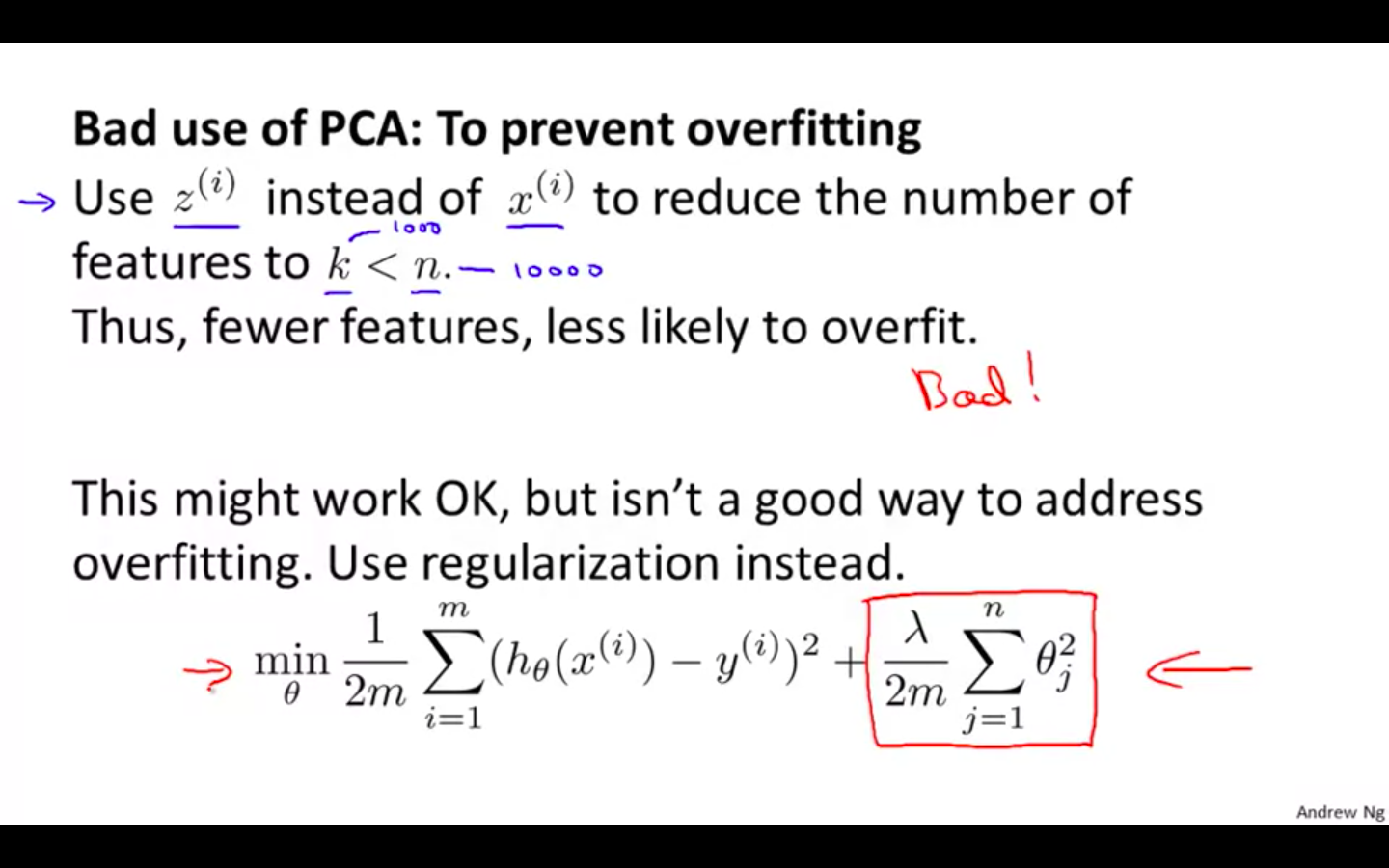
-
Where it shouldn’t be used
